1) United States
The 275,000 registered pharmacists in the United States must all undertake hours-based continuing education to maintain their licence. North Carolina, Iowa and New Mexico have also established a continuing professional development framework as an alternative.
2) United Kingdom
The Higher Education Funding Council for England announced in October 2014 that there would be no control on student numbers implemented at England’s schools of pharmacy, despite predictions of an oversupply of between 11,000 and 19,000 pharmacists by 2040.
3) Senegal
The African region has the most intense pharmacy workforce crisis, with an average of only 0.55 pharmacists per 10,000 population. This lack of human resource has been highlighted during the ongoing Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa.
4) Egypt
Egypt has the highest number of pharmacies per capita of the countries surveyed with 6.66 pharmacists per capita.
5) Pakistan
Around 55% of Pakistan’s 12,000 pharmacists work in the pharmaceutical industry, which has grown rapidly since independence in 1947 and now comprises around 400 pharmaceutical manufacturing units, including 25 multinationals.
6) Japan
There are no pharmacy technicians in Japan, which could explain the high number of pharmacists per capita. However, in 2006, the Japanese government introduced registered salespersons who can sell second- and third-class over-the-counter drugs.
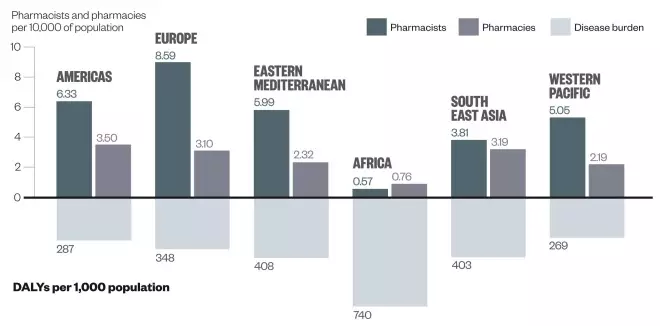
Number of pharmacies relative to global burden of disease
Source: FIP-RPS Global Workforce Observatory; 2012 FIP Global Pharmacy Workforce Report.
Number of pharmacies relative to global burden of disease
The World Health Organization (WHO) African region has the least pharmacies per 10,000 population despite bearing about 30% of the global burden of disease. It also has more pharmacies than there are licensed pharmacists. The country with the lowest burden of disease, measured as disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) per 1,000 population, is Singapore (144) and that with the highest is Sierra Leone (1,177).

Number of pharmacy graduates per 10000 population
Source: FIP-RPS Global Workforce Observatory; 2012 FIP Global Pharmacy Workforce Report.
Number of pharmacy graduates per 10000 population
In 2012, Albania, which has a population of only 3.2 million, produced the most graduates per 10,000 population at 557 from its seven schools of pharmacy. However, only 64 pharmacists gained their licence, giving a total of 1,465 licensed pharmacists. India produced the highest number of graduates, at 70,000 from 1,400 schools, but its population of 1.2 billion puts it ninth in the list.
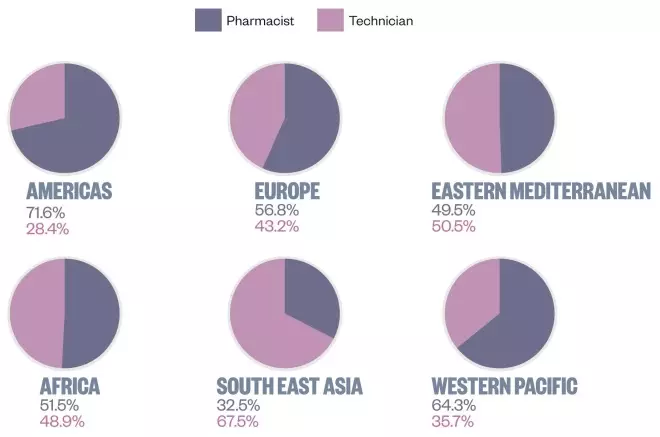
Pharmacy support workforce
Source: FIP-RPS Global Workforce Observatory; 2012 FIP Global Pharmacy Workforce Report.
Pharmacy support workforce
In several countries, such as Japan, support staff are non-existent whereas in others, such as Pakistan, technicians make up more than two-thirds of the workforce.
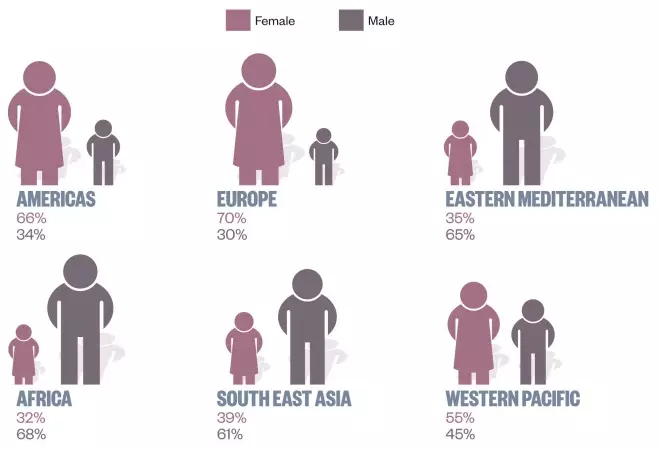
Gender distribution in global pharmacy workforce
Source: FIP-RPS Global Workforce Observatory; 2012 FIP Global Pharmacy Workforce Report.
Gender distribution in global pharmacy workforce
Women make up an average of 54.9% of the workforce but the proportion varies considerably between countries, ranging from 4.8% in Somalia to 92.4% in Croatia.