Alamy Stock Photo / Science Photo Library
This year, clinical articles published in The Pharmaceutical Journal and sister title Clinical Pharmacist have reflected some of the clinical challenges that pharmacists face, and enabled further development of skills relevant to pharmacy practice.
Our quiz highlights some of 2018’s most important topics. You can refresh your knowledge, read these articles in full and access our complete library of CPD articles at www.pharmaceutical-journal.com. The answers to the quiz can be found at the end of this article.
- Skin conditions
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Women’s health
- Immune system diseases
- Diabetes
- Nervous system disease
- Mental health
- Cancer
- Stroke
- Menopause
1. Skin conditions
An 18-year-old patient presents with small (1–10mm) oval, scaly, red-to-pink plaques covering the majority of their body (see image). During full history taking, they tell you that they have recently had a streptococcal throat infection. Which of the following would you diagnose?
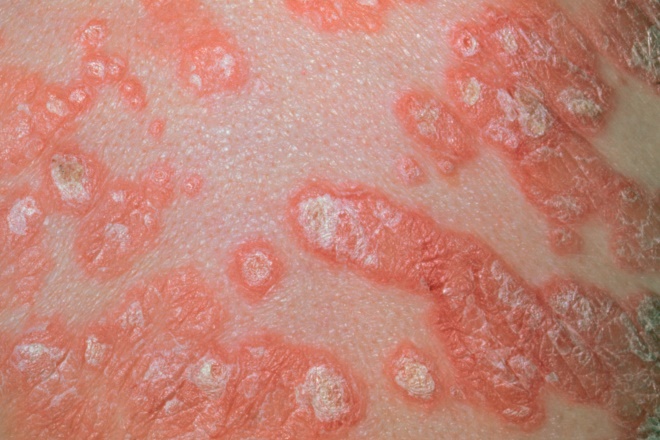
Source: Jim West / Science Photo Library
A: Erythrodermic psoriasis
B: Guttate psoriasis
C: Inverse psoriasis
D: Generalised pustular psoriasis
From: ‘Assessment and management of psoriasis in adults in primary care
’
2. Sexually transmitted infections
Which of the following regimens is the recommended first-line treatment for adults with early syphilis (primary, secondary or latent [<2 years]) who are not penicillin allergic and for whom there are no concerns around adherence?
A: Erythromycin 500mg, four times per day for 14 days
B: Amoxicillin 500mg orally, four times per day plus probenecid 500mg for 14 days
C: Procaine penicillin G, 600,000 units intramuscularly daily for ten days
D: Benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units intramuscularly as a single dose
From: ‘Syphilis: diagnosis and management options’
3. Women’s health
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends which of the following as a first-line treatment option for the pharmacological management of heavy menstrual bleeding if long-term management (≥12 months) is expected?
A: Tranexamic acid 500mg at a dose of 1g three to four times per day at the onset of heavy menstrual bleeding for a maximum of four days
B: Combined oral contraceptives as per individual product information with a maximum of three packets taken consecutively without pill-free weeks
C: Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system 52mg inserted within seven days of the onset of menstruation
D: Norethisterone 5mg three times a day from days 5 to 26 of cycle
From: ‘Heavy menstrual bleeding: diagnosis and management options’
4. Immune system diseases

Source: Hero Images Inc. / Alamy Stock Photo
Cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) is the abnormal response to proteins found in cow’s milk or products containing milk proteins. Reactions can be either immunoglobulin E (IgE) or non-IgE mediated, with IgE-mediated reactions occurring most commonly in formula-fed children or at the onset of mixed feeding. Which of the following symptoms is not indicative of mild-to-moderate IgE-mediated CMPA?
A: Blood or mucus in stools
B: Acute pruritis (itching)
C: Abdominal pain or colic
D: Urticaria (hives)
From: ‘Cow’s milk protein allergy in children: identification and treatment’
5. Diabetes

Source: Jim West / Science Photo Library
In people with type 1 diabetes mellitus, self-monitoring of blood glucose is normally advised at least four times per day (before each meal and at bedtime). How many times per day should this occur during periods of illness, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and before, during and after sport?
A: 7
B: 8
C: 9
D: ≥10
From: ‘Diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes mellitus’
6. Nervous system disease
Levodopa is the gold standard treatment when motor symptoms impact on quality of life in people with Parkinson’s disease, but which of the following statements relating to its potential benefits or harms is incorrect?
A: It gives greater improvement in motor symptoms
B: It has fewer motor complications
C: It gives greater improvement in activities of daily living
D: It has fewer specified adverse events
From: ‘Parkinson’s disease: management and guidance
’
7. Mental health
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most widely prescribed type of antidepressants and are generally well tolerated, but they are not free from side effects. Which of the following is not a common side effect associated with SSRI use?
A: Suicidal ideation
B: Nausea
C: Increased agitation
D: Insomnia
From: ‘Depression in children and young people: identification and management’
8. Cancer
The nature and severity of immune-related toxicities can vary depending on the patient, drug or combination of drugs used. Inhibition of programmed death receptor-1, as well as the ligand of this receptor, is associated with around a 12–37% incidence of immune-related adverse events, but which of the following is most commonly reported?
A: Rashes
B: Diarrhoea
C: Fatigue
D: Liver toxicity
From: ‘Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer: pharmacology and toxicities’
9. Stroke
Strokes can be classified into two main types: ischaemic (i.e. caused by a clot in a blood vessel in the brain) or haemorrhagic (i.e. caused by a bleed in the brain), with risk factors for stroke classified as modifiable or non-modifiable. Which of the following is not a modifiable risk factor for haemorrhagic stroke?
A: Illegal drug use (especially cocaine and crystal meth)
B: Cigarette smoking
C: Heavy drinking
D: Anticoagulation
From: ‘Stroke: classification and diagnosis’
10. Menopause

Source: Alamy.com
A 49-year-old patient on tamoxifen following treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer presents and complains of experiencing hot flushes and night sweats. She has already tried some herbal preparations, but they did not help. Which of the following treatment options for relief of her symptoms would be most appropriate, given her clinical history?
A: Use of a transdermal patch or gel
B: A selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor
C: St John’s wort
D: Venlafaxine prescription
From: ‘Treatment options for menopausal symptoms
’
| Answers | |
|---|---|
| 1. B | 6. B |
| 2. D | 7. A |
| 3. C | 8. C |
| 4. A | 9. B |
| 5. D | 10. D |


