CDC
GPs and internet pharmacies that provide access to online prescribing services should review their gonorrhoea treatment protocols to ensure they comply with national recommendations, say chief medical officer Dame Sally Davies and chief pharmaceutical officer Keith Ridge.
In a letter sent to all GPs and online pharmacies on 18 December 2015, the chief officers highlight a recent outbreak of gonorrhoea in Leeds that was highly resistant to azithromycin.
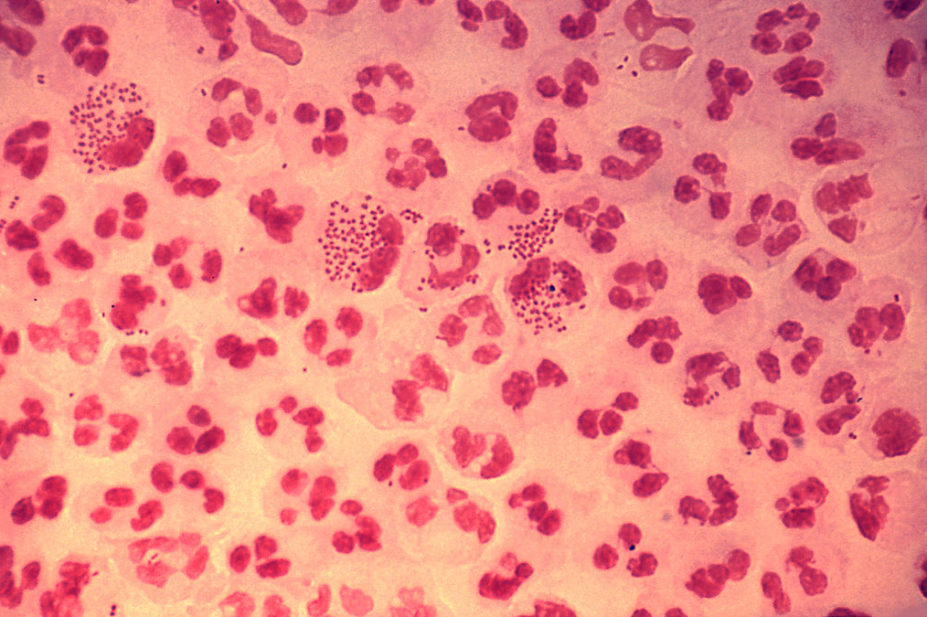
Gonorrhoea is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the UK. And the disease is able to develop resistance to antibiotics rapidly.
“It is therefore extremely important that suboptimal treatment does not occur and, if services lack facilities to provide injectable drugs, patients are referred to a genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinic or sexual health service for management,” says the letter.
Davies and Ridge ask that healthcare professionals ensure their prescribing adheres to guidelines set out by the British Association for Sexual health and HIV. Since 2011, the recommended first-line treatment for gonorrhoea has been a combination of injectable ceftriaxone and oral azithromycin. Dual therapy is recommended because gonorrhoea is highly unlikely to develop resistance to two antibiotics simultaneously.
In 2015, 14 cases of gonorrhoea with high-level azithromycin resistance were identified in a continuing outbreak in Leeds. So far, all isolates remain susceptible to ceftriaxone. However, Davies and Ridge say the outbreak highlights the importance of “effective antimicrobial stewardship for all prescribing” for this infection.