M. Welland
Glioblastoma, the most common and aggressive form of adult brain cancer, has a high mortality rate. Even when initial treatment proves successful, treatment resistance rapidly develops.
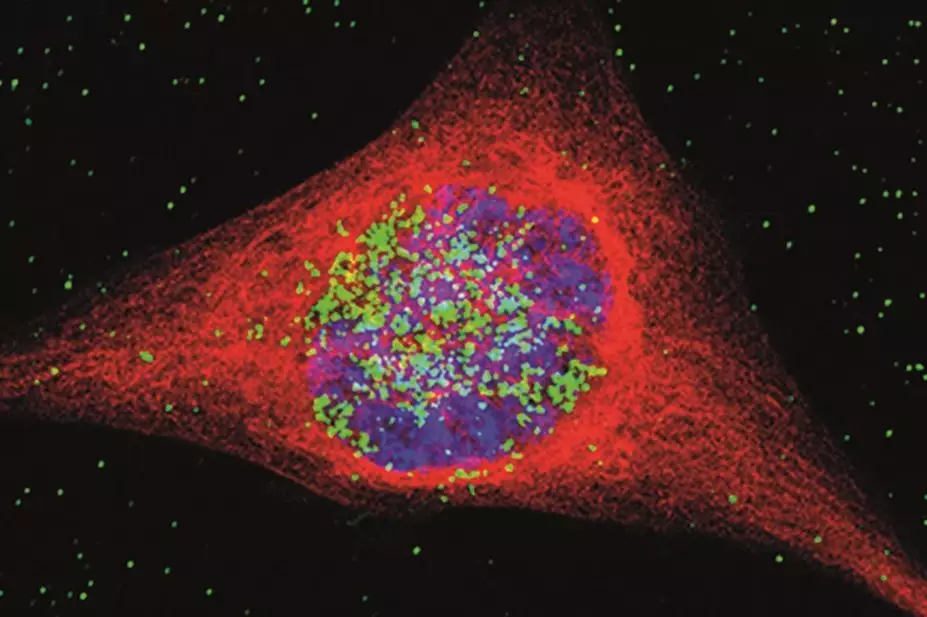
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed gold nanoparticles containing cisplatin as part of a twofold attack on the cancer. Once the nanoparticles are taken up by the cells, cisplatin causes DNA damage and cell death. This effect is enhanced with radiotherapy, which stimulates the gold particles to release electrons that cause further damage.
Using multidrug resistant cells taken from gliobastoma patients, the researchers have successfully destroyed the diseased cells without treatment resistance emerging, according to results published in Nanoscale (online, 25 July 2014)[1]
. The next stage of the research will look at how to make this approach applicable to patients.