Science Photo Library and Wkimedia Commons
During 2015, The Pharmaceutical Journal and sister title Clinical Pharmacist have covered a wide range of clinical topics relevant to pharmacists of all sectors and experience. From migraine to advanced stage cancers, our coverage reflects the range of clinical challenges pharmacists face.
Test your knowledge on the subjects we have covered. If you find any gaps in your knowledge, visit pharmaceutical-journal.com, where you can find these and a library of many more CPD articles designed to improve your practice skills. You can also take a 15-question quiz on many of these subjects to check your understanding and then print off a certificate if you pass the assessment.
1. Diuretic therapy
2. Iron deficiency anaemia
3. Liver impairment
4. Burns
5. Hormonal contraception
6. Helminth infections
7. Penicillin allergy
8. Warts
9. Scarlet fever
10. Lubiprostone interactions
1. Diuretic therapy
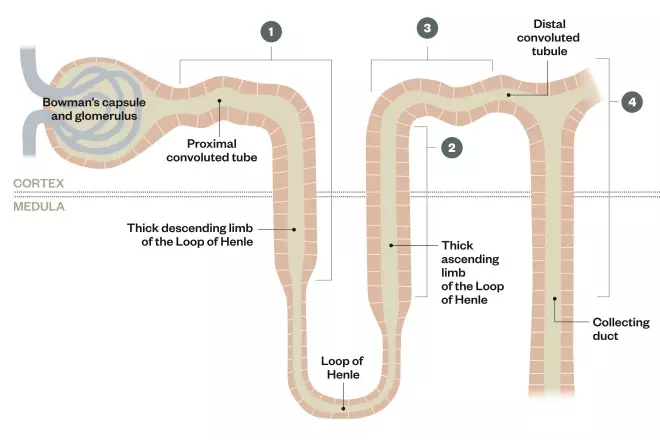
Diuretics are commonly used to treat oedema caused by conditions such as heart failure, liver cirrhosis and kidney disease. Different classes of diuretic have distinct sites of action which determines their effectiveness and side effect profile. Which of the following numbered points represents the site of action for thiazides and related diuretics?
A: 1
B: 2
C: 3
D: 4
From:
Diuretic therapy explained
2. Iron deficiency anaemia
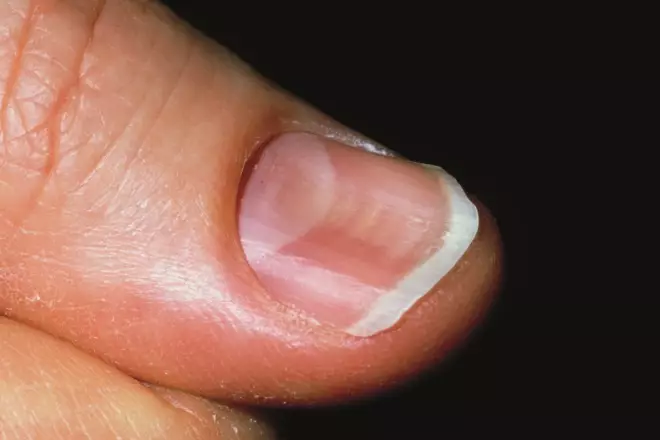
Source: Science Photo Library
Koilonychia, or spoon nails (pictured), is a rare, but indicative sign of severe iron deficiency anaemia. Patients with suspected iron deficiency anaemia should be referred to their GP who will order blood tests. In patients with no co-existent inflammatory disease, which of the following is the most consistent reliable indicator of iron deficiency anaemia?
A: Reduced mean cell haemoglobin
B: Low ferritin
C: Low reticulocyte haemoglobin
D: Reduced mean cell volume
From:
Iron deficiency anaemia: basic management
3. Liver impairment
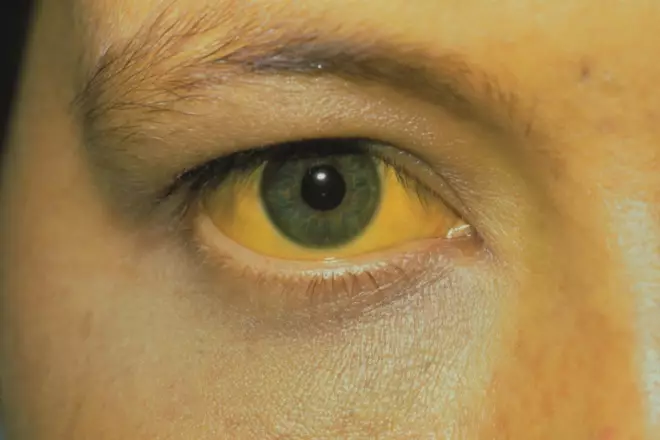
Source: Science Photo Library
Jaundice, or the yellowing of the skin and eyes, caused by the build-up of bilirubin (pictured) is a sign of liver disease. Many types of medicines can be affected by liver disease, but which of the following types precipitate or worsen encephalopathy in patients with liver disease?
A: Constipating and sedating medicines and medicines that cause gastrointestinal ulceration
B: Constipating and sedating medicines and medicines with a high sodium content
C: Constipating and sedating medicines and medicines that are nephrotoxic
D: Constipating and sedating medicines and medicines that affect fluid-electrolyte balance
From:
Liver impairment: ensuring medicines safety
4. Burns
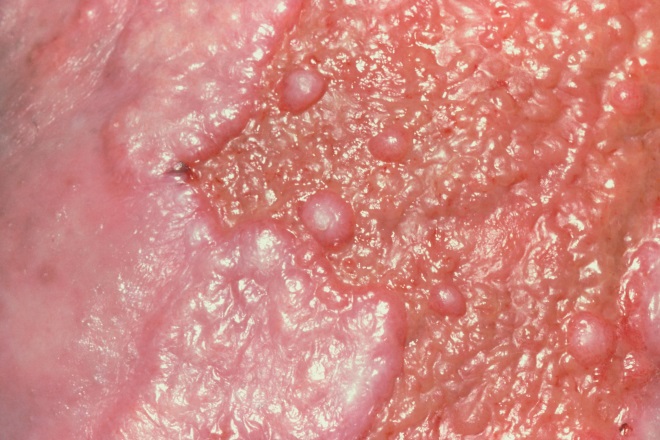
Source: Science Photo Library
Quick action is required with burns to minimise tissue damage and prevent infection. A patient presents after suffering a burn (pictured) that has affected the whole epidermis and deep layers of the dermis. Which one of the following types of burn has the patient sustained?
A: Superficial
B: Partial thickness-superficial
C: Partial thickness-deep dermal
D: Full thickness
From:
Burns: assessment and treatment
5. Hormonal contraception
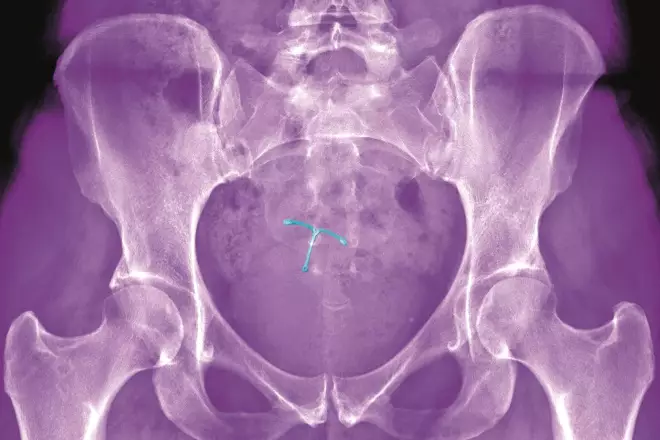
Source: Science Photo Library
There are currently three available methods for emergency hormonal contraception: copper intrauterine devices (pictured), levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate. Which of the following statements about emergency hormonal contraception is true?
A: Copper intrauterine devices are more effective as emergency contraception than levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate
B: Levonorgestrel is more effective as emergency contraception than ulipristal acetate and copper intrauterine devices
C: Ulipristal acetate is more effective as emergency contraception than levonorgestrel and copper intrauterine devices
D: Copper intrauterine devices, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate have similar effectiveness as emergency contraceptives
From:
Hormonal contraception: methods and patient eligibility
6. Helminth infections
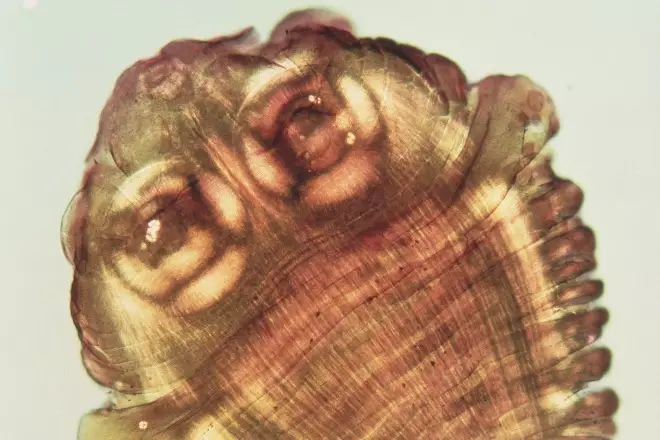
Source: Science Photo Library
Taenia saginata, or beef tapeworm (pictured), causes taeniasis. Patients are usually asymptomatic and often only present after having passed a proglottid segment in stools. After laboratory confirmation of species, for adults aged over 18 years, treatment should commence with which of the following drug regimens?
A: Albendazole 15mg/kg or praziquantel (unlicensed indication) 10mg/kg immediate dose
B: Niclosamide 2g immediate dose or praziquantel (unlicensed indication) 10mg/kg immediate dose
C: Albendazole 400mg immediate dose or mebendazole 500mg immediate dose
D: Ivermectin (unlicensed) 150–200µg/kg
From:
Helminth infections: diagnosis and treatment
7. Penicillin allergy
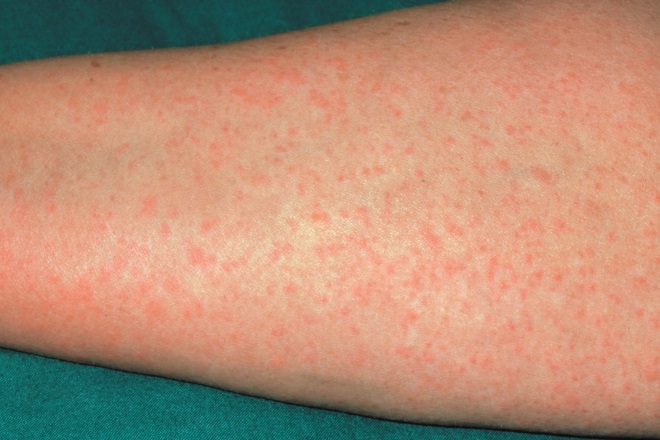
Source: Science Photo Library
All forms of natural and semisynthetic penicillins, or drugs with similar structures can cause allergy (pictured). A patient with a documented history of a penicillin allergy causing an itchy rash has been diagnosed with a bacterial respiratory tract infection. Which of the following treatment options can be considered?
A: Meropenem
B: Cefruxamine
C: Cefazolin
D: Clarithromycin
From:
Penicillin allergy: identification and management
8. Warts
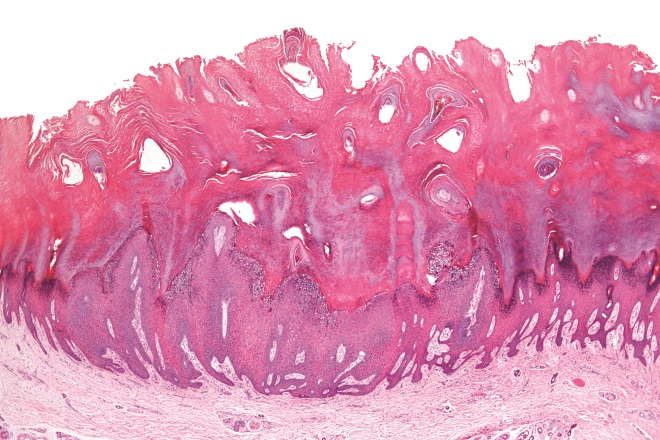
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Warts (pictured) are common viral skin conditions caused by human papilloma virus. Treatment options include salicylic acid, often in combination with lactic acid, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde and cryotherapy. Which of the following statements regarding treatments is true?
A: Salicylic acid can be applied to warts on the face
B: Salicylic acid can be used to treat plantar warts in patients with diabetes
C: Salicylic acid can be used to treat warts in pregnancy but only on a small area for a limited period of time
D: Salicylic acid is the treatment of choice for young children
From:
Warts and verrucas: assessment and treatment
9. Scarlet fever
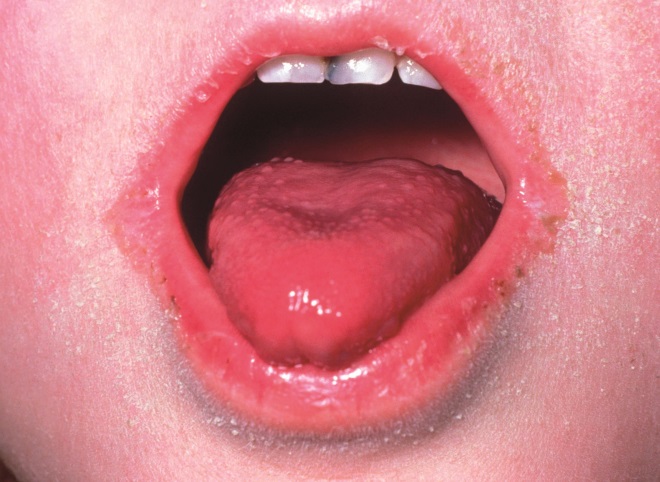
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Scarlet fever is caused by toxin-producing strains of Streptococcus pyogenes, or group A streptococcus. Patients with scarlet fever present with circumoral pallor around the mouth and a ‘strawberry tongue’ (pictured). If not treated with antimicrobials, how long can a patient remain infectious after the onset of symptoms?
A: 7–10 days
B: 10–12 days
C: 14–21 days
D: 25–30 days
From:
Scarlet fever: acute management and infection control
10. Lubiprostone interactions
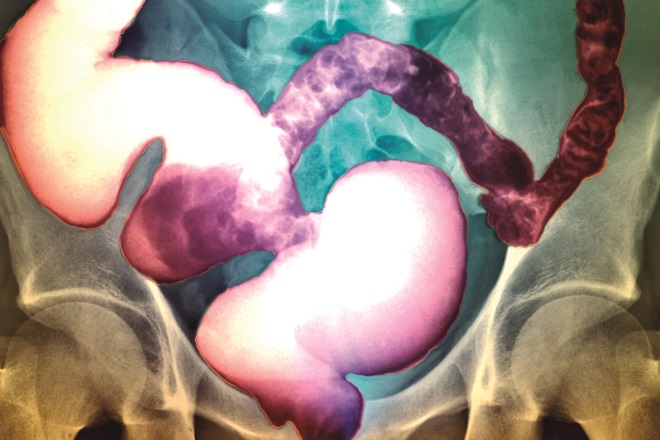
Source: Science Photo Library
Lubiprostone is licensed in the UK for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation in adults (pictured). Which of the following statements about lubiprostone interactions is true?
A: Taking lubiprostone with food may reduce any nausea
B: The efficacy of oral contraceptives may be reduced if used concurrently
C: The concurrent use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases the risk of diarrhoea
D: The efficacy of lubiprostone may be increased by diphenylheptane opioids
From:
Linaclotide, lubiprostone and prucalopride interactions
| Answers | |
|---|---|
| 1. C | 6. B |
| 2. B | 7. D |
| 3. D | 8. C |
| 4. C | 9. C |
| 5. A | 10. A |
You might also be interested in…
Highlights of CPD and learning in 2016
Test yourself: the 2020 CPD and learning quiz