Science Photo Library and Innovative Eye Care
This year The Pharmaceutical Journal and sister title Clinical Pharmacist have published articles that cover a wide range of clinical topics, from eye diseases to anticoaglation. Our coverage reflects both the clinical challenges pharmacists face, as well as focusing on further developing key skills relevant to practice.
Our quiz highlights some of 2016’s most important topics. You can refresh your knowledge by reading these articles in full at pharmaceutical-journal.com, as well as accessing our full library of CPD articles. The answers to this year’s quiz can be found at the bottom of this article.
1. Gastroenterology
2. Religious considerations
3. Respiratory disease
4. Medicine reconciliation
5. Eye diseases
6. Lipid disorders
7. Renal
8. Anticoagulants
9. Endocrine system diseases
10. Eye disases
11. Mental health conditions
12. Autoimmune diseases
13. Respiratory disease
14. Medication formulations
15. Antimicrobials
1. Gastroenterology
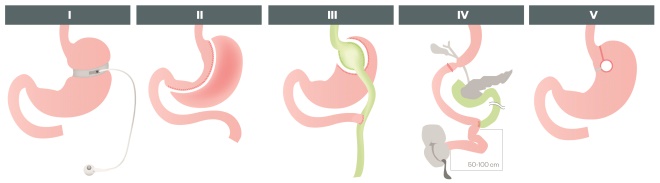
Source: The Pharmaceutical Journal
The prevalence of obesity has continued to dramatically increase over the past few decades. Bariatric surgery is a treatment option for patients who are obese. Which of the following options correctly label the different types of bariatric surgery procedures (pictured)?
A: I. Adjustable gastric band; II. Vertical banded gastroplasty; III. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; IV. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch; V. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy
B: I. Vertical banded gastroplasty; II. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; III. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy; IV. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch; V. Adjustable gastric band
C: I. Adjustable gastric band; II. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy; III. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; IV. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch; V. Vertical banded gastroplasty
D: I. Adjustable gastric band; II. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy; III. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch; IV. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; V. Vertical banded gastroplasty
From:
Bariatric surgery and the effects on drug pharmacokinetics
2. Religious considerations

Source: Courtesy of Green Light Pharmacy, Euston
Muslims fast from dawn until dusk during Ramadan. Eating, drinking (including water), and administration of medicines orally and intravenously are prohibited during this time. Which of the following changes do not occur to the body during fasting?
A: The body generates its own energy by burning stored excess fats, carbohydrates and sugars to produce energy
B: During early fasting there is a high rate of gluconeogenesis with amino acids as the primary substrates
C: Progressive ketosis develops because of the mobilisation and oxidation of fatty acids
D: There is an increase in insulin
From:
How pharmacists can support and advise patients during Ramadan
3. Respiratory disease
Source: Illustration by Javier Trigo
Inhaled medicines are the cornerstone of asthma management, however, evidence suggests that many patients are unable to use their inhalers effectively. Which of the following is not a common inhaler technique error?
A: Holding your breath after inhalation
B: Using an empty inhaler
C: Not priming the aerosol inhaler device
D: Not shaking an aerosol inhaler device before use
From:
How to help patients optimise their inhaler technique
4. Medicine reconciliation

Source: Shutterstock.com
Without an accurate medication history, prescribers may inadvertently make incorrect decisions about a patient’s treatment. Which of the following statements about taking a detailed medication history is true?
A: Only GP surgeries can provide the most up-to-date medicine list for the patient
B: Extra care should be taken when reviewing medicine administration record (MAR) sheets with handwritten additions or amendments and those that do not indicate how many pages make up the MAR sheet
C: Once an accurate medication history has been obtained, this information does not need to be documented in the patient’s medical notes
D: It is OK to assume that any medicines brought in by the patient are their own
From:
How to take an accurate and detailed medication history
5. Eye diseases
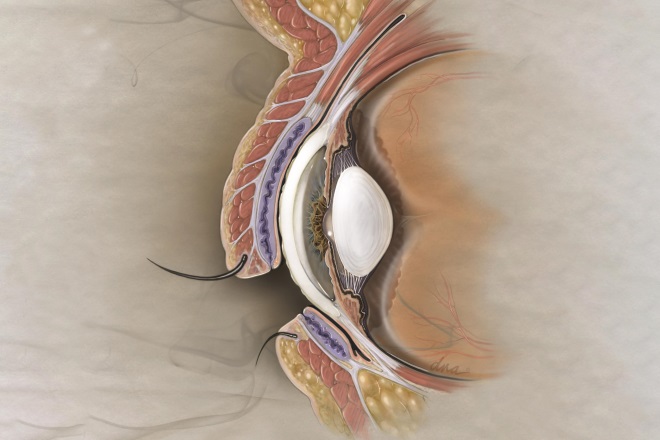
Source: Alex Baker
Dry eye is a common ocular condition. Which of the following statements about treatment options is true?
A: Hypromellose is cost effective and readily available both in preserved and non-preserved formulations
B: Reducing dietary omega-3 fatty acid intake can reduce the symptoms of dry eye
C: If products are used in conjunction with other eye drops or eye ointments, the most viscous products should be applied first
D: Products containing preservatives are licensed for use with contact lenses and so do not cause irritation
From:
Recommending dry eye treatments in community pharmacy
6. Lipid disorders
Source: Science Photo Library
Non-statin drugs can be prescribed for the management of dyslipidaemia in adults. Which of the following statements are true?
A: Ezetimibe should be prescribed at a dose of 10mg daily and can be taken at any time of the day, with or without food
B: Lomitapide should be initiated at a low 5mg dose that is increased gradually every four days to a maximum of 50mg daily
C: High doses of Omacor (5g daily), an omega-3 fatty acid supplement, are needed to lower triglycerides
D: Colesevelam, a bile acid binder, is a first-line option for the management of dyslipidaemia
From:
Non-statin drugs for the management of dyslipidaemia in adults
7. Renal
Source: Science Photo Library
Chronic Kidney Disease – Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) is used to describe the pathophysiological changes that occur in the vascular and skeletal system in CKD. Which of the following statements is true?
A: If a patient has both liver and renal disease, calcitriol would be the treatment of choice for hyperparathyroidism, because 1α-hydroxy vitamin D3 still requires hepatic hydroxylation
B: Calcium and vitamin D products should be used in patients with calciphylaxis
C: The suggested first line phosphate binder for the treatment of hyperphosphataemia is calcium carbonate
D: Patients on doxycycline should avoid taking calcium acetate within two hours
From:
Chronic Kidney Disease – Mineral and Bone Disorder: pathophysiology and treatment
8. Anticoagulants
Source: Science Photo Library
Formal bridging of anticoagulation involves the substitution of oral anticoagulation with a short-acting alternative, usually low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), during the perioperative period. Which of the following statements is true?
A: In an emergency, patients on warfarin can be given 6mg of vitamin K intravenously to reduce the international normalised ratio (INR) within five hours
B: For patients at moderate thrombotic risk, no bridging is required and a prophylactic dose of LMWH only should be used
C: Full dose anticoagulation with LMWH can be started 24 hours post-operatively after a high risk procedure
D: In patients undergoing cataract surgery, oral anticoagulant therapy may be continued prior to the procedure
From:
Bridging anticoagulation: perioperative management of patients on anticoagulants
9. Endocrine system diseases
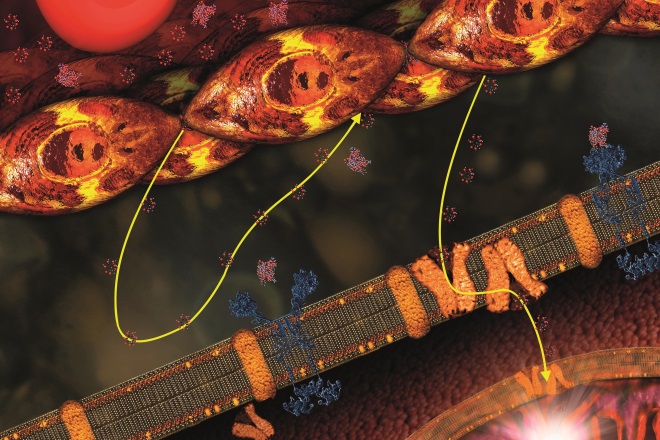
Source: Science Photo Library
In diabetes mellitus, insulin levels (and the related feedback system) are abnormal. Which of the following statements is correct?
A: Patients newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes should be offered the option of non-basal bolus regimens
B: Insulin dosing should ‘start low and go slow,’ eventually rising to a daily insulin requirement of 0.5–1.5 units/kg per day (on average)
C: Analogues closely mimic normal insulin release and are favoured for patients with type 1 diabetes
D: The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends two injections of neutral protamine hagedorn (NPH) insulin a day, which can be titrated to three injections a day if necessary
From:
Insulin initiation in patients with diabetes
10. Eye diseases
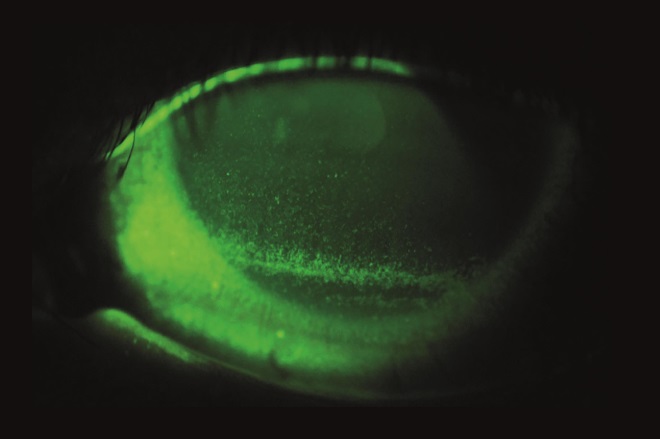
Source: Courtesy of Innovative Eye Care
Differential diagnosis of dry eye is important to exclude conditions that have similar signs or symptoms. Which of the following symptoms indicates that the patient has dry eye, rather than another condition?
A: Burning
B: Stickiness, crusting and discharge of the eye
C: Itchiness
D: Dry mouth and other mucosal tissues (e.g. swollen salivary glands for more than three months)
From:
Identification of dry eye conditions in community pharmacy
11. Mental health conditions
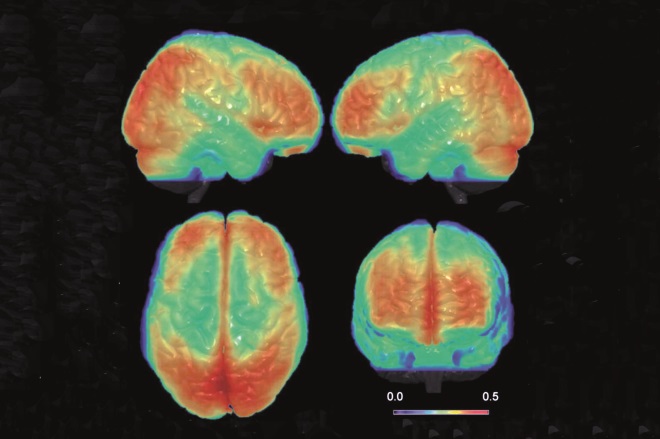
Source: Science Photo Library
Bipolar disorder or bipolar affective disorder (BPAD) is a mood disorder characterised by extreme switches between depressive and manic episodes. Which of the following statements about treatment is correct?
A: Lamotrigine is recommended in patients with hypomania
B: In maintenance therapy, carbamazepine is better tolerated for short-term use and valproate is better suited for long-term therapy
C: The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends a combination of fluoxetine and olanzapine as the most clinically- and cost-effective treatment option for moderate or severe bipolar depression
D: A patient with a history of bone marrow depression and bipolar disorder that is unresponsive to lithium can be prescribed carbamazepine
From:
Bipolar disorder: pharmacotherapy options with a focus on women of childbearing age
12. Autoimmune diseases
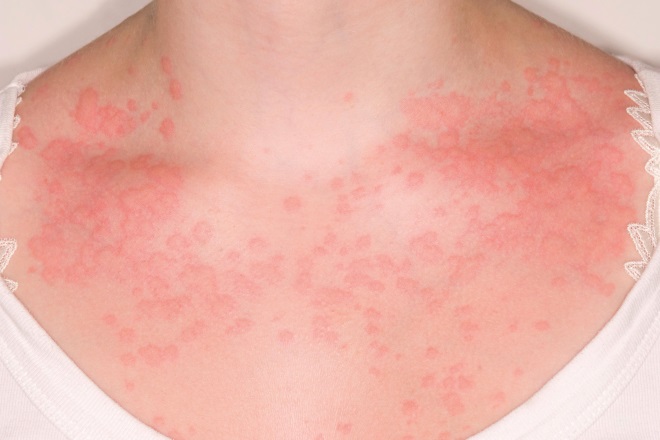
Source: Science Photo Library
Urticaria (pictured) is characterised by a red, raised, itchy whealing rash, with or without angioedema. Which of the following statements about treating urticaria is true?
A: Mycophenolate can be prescribed (off-licence) at 2,000mg twice daily with a non-sedating H1-antihistamine in patients with severe chronic spontaneous urticaria
B: Sedating H1-antihistamines should be avoided for chronic use as they interfere with psychomotor performance
C: Patients with corticosteroid-dependent chronic spontaneous urticaria can be prescribed methotrexate at a starting dose of 10mg twice a week with co-prescription of folic acid 5mg twice a week (on the same days)
D: In patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria where symptoms are not being controlled by one non-sedating H1-antihistamine, a combination of H1– and H2-antihistamines should be prescribed
From:
Chronic spontaneous urticaria: clinical features, diagnosis and management
13. Respiratory disease
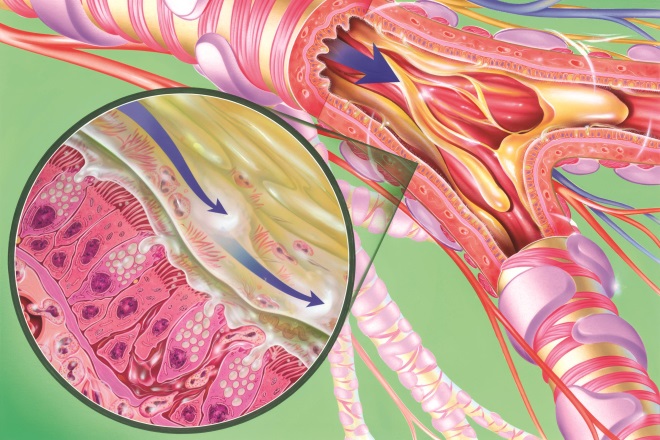
Source: Science Photo Library
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterised by the presence of incompletely reversible airflow obstruction. Which of the following statements about COPD is true?
A: Current COPD guidelines recommend the use of an inhaled corticosteroid with a long-acting muscarinic antagonist and long-acting B2 -agonist in patients with predominant exacerbator phenotype
B: Monotherapy with inhaled corticosteroids is recommended in patients with mixed COPD-asthma phenotype
C: Management of patients with predominant exacerbator phenotype focuses on reducing exacerbations and includes flu vaccination, stopping smoking and pulmonary rehabilitation
D: A patient with a post-bronchodilator FEV1 value of 65% predicted for their age, height and gender indicates that their chronic obstructive disease state is severe
From:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: clinical phenotypes and implications for management
14. Medication formulations
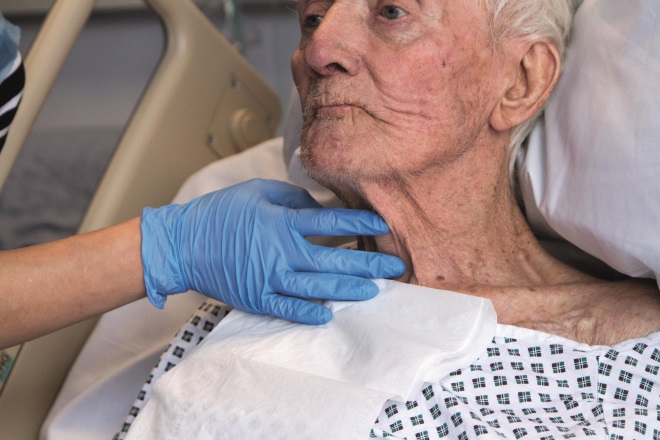
Source: Science Photo Library
Dysphagia is the term used to describe a swallowing disorder usually resulting from a neurological or physical impairment of the oral (mouth), pharyngeal (upper throat) or oesophageal (lower throat) mechanisms. Which of the following statements is true?
A: All patients with dysphagia cannot swallow solid oral formulations (whole tablets and capsules) and need to be prescribed liquids
B: Dysphagia in patients with silent aspiration is more difficult to identify and these patients are more likely to develop aspiration pneumonia
C: Thinner liquid medicines decrease the risk of coughing and aspiration in a patient with dysphagia
D: When prescribing for a patient with dysphagia, it is not necessary to perform a medication review
From:
How to tailor medication formulations for patients with dysphagia
15. Antimicrobials
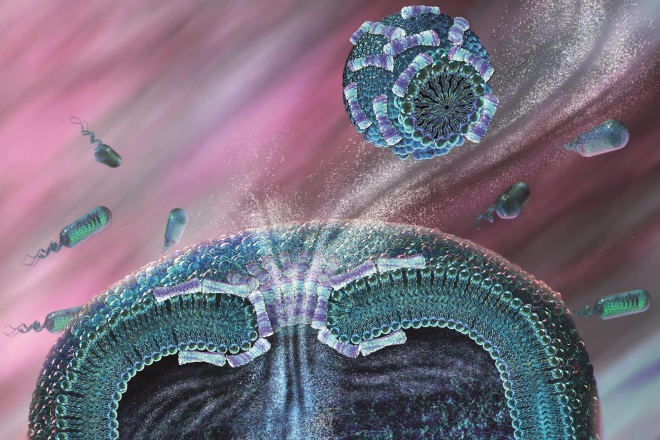
Source: Science Photo Library
The increase of antimicrobial resistance represents a major global health problem. Which of the following statements is true?
A: A patient who has been prescribed intravenous antibiotics, who is clinically improving, can be switched to an oral equivalent after 24 hours
B: Certain drugs should always be prescribed in combination (e.g. rifampicin and fusidic acid) because the use of these drugs individually can result in the emergence of resistant bacteria
C: Prescribing benzylpenicillin alone is favourable for patients with infective endocarditis
D: Antibiotics should never be prescribed during pregnancy
From:
Principles of initiating antimicrobial therapy and empiric prescribing
| Answers | |
|---|---|
| 1. C | 9. C |
| 2. D | 10. A |
| 3. A | 11. C |
| 4. B | 12. B |
| 5. A | 13. C |
| 6. A | 14. B |
| 7. A | 15. B |
| 8. D | |
You might also be interested in…
Highlights of CPD and learning in 2015
Test yourself: the 2020 CPD and learning quiz