
Mclean/Shutterstock/Science Photo Library/Wendy K Smith
This year, we launched our essential resources platform — a hub of content published in The Pharmaceutical Journal, broken down by clinical area, to help pharmacists quickly and easily expand their knowledge.
For our 2019 end-of-year quiz, we have done something similar. Topics have been broken down by clinical area to help you not only identify potential areas of focused learning for revalidation, but also to help you find the answers you need to improve your knowledge.
The answers to the quiz can be found at the end of this article.
Infectious diseases
1. According to the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV’s national guidelines, which of the following is the first-line treatment option for an uncomplicated Mycoplasma genitalium infection?
A: Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 7 days, followed by azithromycin 1g orally, single dose, azithromycin 500mg orally once per day for 2 days
B: Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 10 days, followed by azithromycin 1g orally, single dose, azithromycin 500mg orally once per day for 2 days
C: Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 14 days, followed by azithromycin 1g orally, single dose, azithromycin 500mg orally once per day for 2 days
D: Moxifloxacin 400mg taken orally once per day for 14 days
E: Moxifloxacin 400mg taken orally once per day for 10 days
From: ‘
Antibiotic treatment of Mycoplasma genitalium infection
’
2. According to The European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, the European Confederation of Medical Mycology and the European Respiratory Society joint clinical guidelines, which of the following is the first-line treatment option for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis?
A: Amphotericin B
B: Echinocandins
C: Isavuconazole
D: Posaconazole
E: Voriconazole
From: ‘Aspergillosis: causes, types and treatment’
3. Guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) indicate that ceftriaxone can be used as an alternative to cefotaxime to treat meningitis in which of the following?
A: Babies (children aged under three months) who are not receiving a calcium infusion
B: Babies with jaundice
C: Babies with hypoalbuminaemia
D: Babies with acidosis
E: Premature babies
From: ‘Case-based learning: meningitis’
4. Which group of people should not receive chemoprophylaxis for malaria?
A: People travelling for more than six months in malaria-endemic countries
B: People who are visiting low-risk areas
C: People who lack normal spleen function
D: People who once lived in endemic areas
E: Pregnant women
From: ‘Advising patients about malaria risks and prevention’
5. Which of the following complications of measles is the least common, but most severe?
A: Conjunctivitis
B: Diarrhoea
C: Otitis media
D: Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
E: Viral pneumonitis
From: ‘Discussing the MMR vaccine with patients’
Mental health
6. Which of the following is not a risk factor commonly linked with increased risk of suicide?
A:
Chronic pain
B: Family history of suicide
C: Being male
D: Previous suicide attempt
E: Severe financial difficulties
From: ‘Suicide: how to recognise the warning signs and deal with disclosure’
7. Which of the following primary presenting features are seen in people with antisocial personality disorder?
A: Flattened emotions
B: Submissive behaviour
C: Social inhibition
D: Suspiciousness of others
E: Violation of the rights and feelings of others
From: ‘Antisocial personality disorder: diagnosis and management’
8. Body dysmorphic disorder is characterised by an individual’s intense preoccupation with one or several aspects of their appearance. What is the NICE-recommended first-line pharmacological treatment?
A: Buspirone
B: Clomipramine
C: Escitalopram
D: Fluoxetine
E: Venlafaxine
From: ‘Recognising and managing body dysmorphic disorder’
Palliative care
9. The Gold Standards Framework recommends considering anticipatory prescribing of subcutaneous formulations as part of advanced care planning for palliative care patients. Which of the following indications does it not recommend this for?
A: Agitation/restlessness
B: Excess respiratory secretions
C: Fatigue
D: Nausea and vomiting
E: Pain
From: ‘Case-based learning: palliative and end-of-life care in community pharmacy’
10. Pruritus can be a distressing symptom for patients with liver disease and can be accompanied with a painful skin-picking disorder. What first-line treatment does the European Association for the Study of the Liver recommended for this symptom?
A: Cetirizine
B: Chlorphenamine
C: Fexofenadine
D: Loratadine
E: Menthol 1% in aqueous cream
From: ‘Palliative management in end-stage liver disease’
Dermatological conditions
11. Acne is a common condition that affects 90% of people during their teenage years. Which of the following options correctly label the different types of acne lesion?
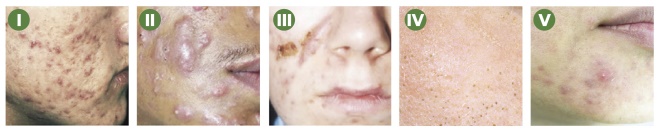
Source: Primary Care Dermatology Society / St Bartholomew’s Hospital / Science Photo Library
A: I. Open comedones; II. Cysts; III. Closed comedones; IV. Pustules; V. Nodules.
B: I. Cysts; II. Pustules; III. Nodules; IV. Open comedones; V. Closed comedones.
C: I. Pustules; II. Nodules; III. Cysts; IV. Open comedones; V. Closed comedones.
D: I. Nodules; II. Cysts; III. Pustules; IV. Closed comedones; V. Open comedones.
E: I. Closed comedones; II. Pustules; III. Nodules; IV. Open comedones; V. Cysts.
From: ‘Case-based learning: acne vulgaris’
12. Which of the following drugs have been strongly associated with a significant increased risk of Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis?
A: Co-trimoxazole
B: Diltiazem
C: Nitrofurantoin
D: Vancomycin
E: Sertraline
From: ‘Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis’
Minor ailments
13. Most coughs are acute and self-limiting; however, they can be a symptom of a more serious condition. Which of the following is not a red flag in a patient with a cough?
A: Considerable breathlessness
B: Cough lasting for less than three weeks
C: Coughing up blood
D: Heartburn
E: Unexplained weight loss
From: ‘Case-based learning: cough’
14. Patients may present in community pharmacy with oral lesions. What condition is depicted below?
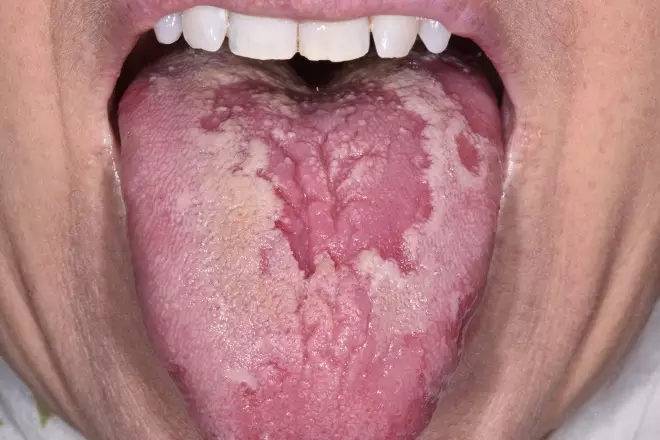
Source: Science Photo Library
A: Geographic tongue
B: Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
C: Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
D: Squamous cell carcinoma
E: Traumatic oral ulcer
From: ‘Oral ulceration: causes and management’
15. An eight-year-old boy with tonsillitis has been prescribed phenoxymethylpenicillin 250mg four times per day for ten days. According to the
BNF
, which of the following is a rare side effect of this treatment?
A: Angioedema
B: Diarrhoea
C: Hypersensitivity
D: Nausea
E: Vomiting
From: ‘Case-based learning: sore throat’

| Answers | |
|---|---|
| 1. a | 9. c |
| 2. e | 10. e |
| 3. a | 11. c |
| 4. b | 12. a |
| 5. d | 13. b |
| 6. b | 14. a |
| 7. e | 15. a |
| 8. d | |


