ISM / Science Photo Library
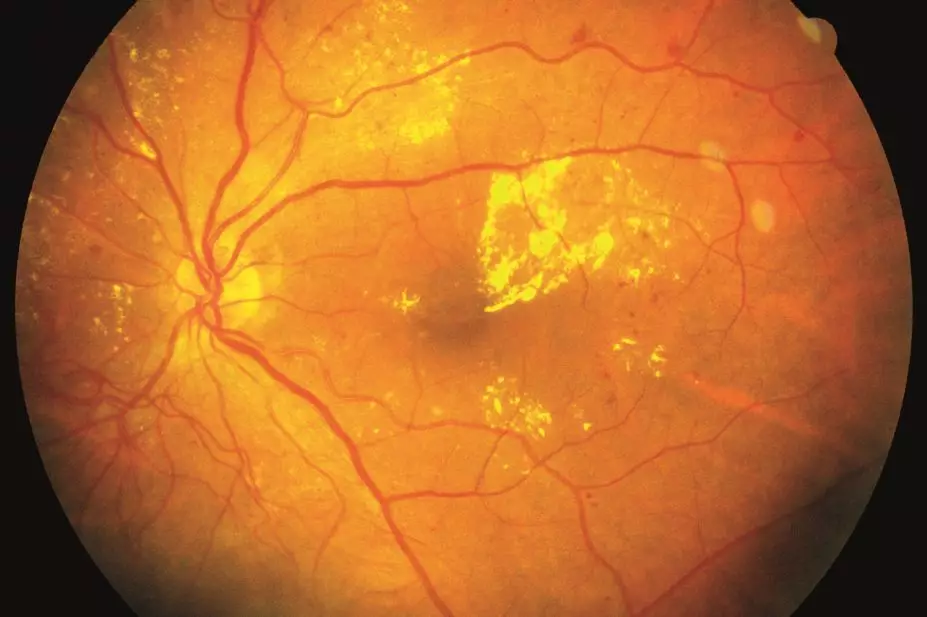
Ranibizumab is a monoclonal antibody fragment used to treat age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic macular oedema (DMO) — a leading cause of vision loss in working-age adults in the United States.
Researchers developed a population-based model to investigate whether wider use of ranibizumab could help prevent sight loss in thousands of adults with diabetic eye disease, and publish their findings in Ophthalmology
[1]
.
Treatment with ranibizumab 0.3mg at 4-week intervals would reduce the incidence of vision impairment (VI) by 45% and legal blindness by 75%, equivalent to nearly 6,500 cases — based on the approximately 37,274 Hispanic and non-Hispanic white adults with DMO in the United States eligible for ranibizumab treatment.
The study was supported by Genentech, developer of ranibizumab.