
Science Photo Library/Shutterstock.com/The Pharmaceutical Journal
Pharmacists working across all sectors are increasingly likely to encounter patients with diabetes, it is therefore vital they have the appropriate knowledge and skills to feel confident when treating this patient population. Work your way through the quiz by expanding the questions in the boxes below.
Each question includes a link to a relevant article published in The Pharmaceutical Journal, providing more information on the topic. When you have answered all the questions, select ‘Finish quiz’ at the bottom of the page to check your score.

Source: Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
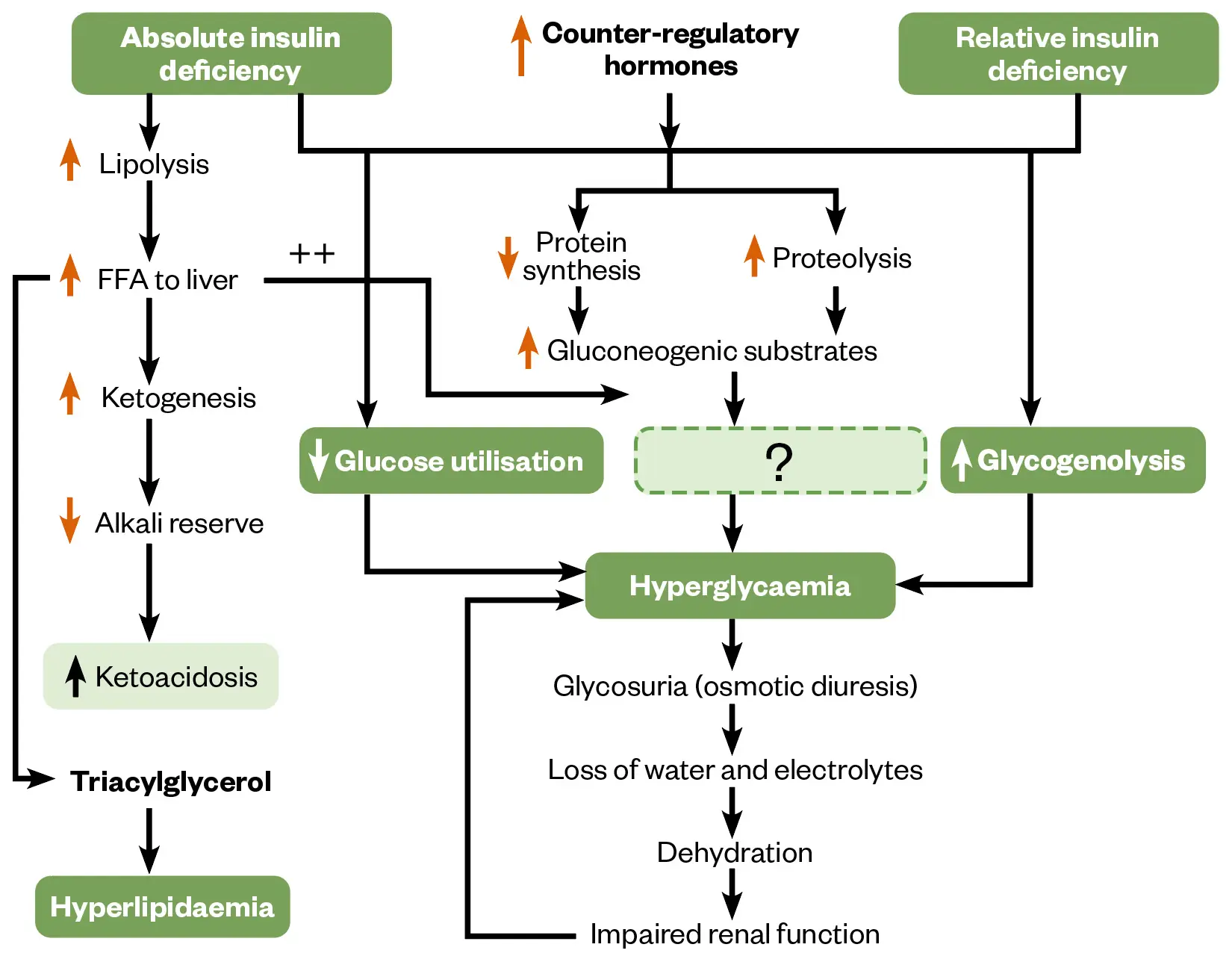
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diagnosis and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diagnosis and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

JOSE CALVO / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

DIGICOMPHOTO/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
The Pharmaceutical Journal
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diabetic ketoacidosis in adults: identification, diagnosis and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diabetic ketoacidosis in adults: identification, diagnosis and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Insulin in practice for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Insulin in practice for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Emotional wellbeing in children and young people with diabetes’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus for glycaemic control’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Case-based learning: insulin intensification in a Hindu patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Perioperative management of type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Perioperative management of type 2 diabetes mellitus’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Acute complications of diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Acute complications of diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
According to the International Diabetes Federation and World Health Organization, which of the following patients would NOT meet the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes mellitus:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
HbA1c is appropriate to be used as a diagnostic tool for patients who are taking steroids — true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous condition resulting from the destruction of what type of cells?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Match the type of insulin with its onset of action:
Sort elements
- 5–10 minutes
- 10–20 minutes
- 15–45 minutes
- 1–2 hours
- Steady state occurs after 2–3 doses
- Ultra rapid-acting insulin aspart
- Rapid-acting insulin glulisine
- Short-acting insulin soluble
- Intermediate-acting isoprene insulin
- Long-acting detemir
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Hyperglycaemia is driven by increases in hepatic and glycogenolysis, paired with a in uptake of glucose into the peripheral tissues.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Which of the following can be precipitating factors of diabetic ketoacidosis?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
A basal-bolus regimen involves multiple injections; short- or rapid-acting insulin is injected before meals and basal insulin is injected once or twice daily. Which of the following statements about basal-bolus regimens are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Fill in the blanks:
Biosimilar insulins are produced when a expires on an insulin, allowing manufacturers to produce copies of the original insulin molecule. There are benefits to using biosimilar insulins; for example, they are less than the parent insulin, and large-scale randomised control trials needed for the parent insulin are not required for the biosimilar insulin — instead, the biosimilar insulin needs to prove to the parent insulin.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
One way that pharmacists can support families living with diabetes is through the language used to talk about the condition.
Match the phrase that may have possible negative connotations with the more appropriate alternative:
Sort elements
- Person with diabetes
- Lives with diabetes
- Glucose check
- In/out of range
- Self-care
- Diabetic/patient
- Suffers from
- Glucose test
- Good/bad numbers
- Control/compliance/adherence
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
GLP-1 therapy should be considered in people with indicators of high risk or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Which of the following is NOT included in the classification of high ASCVD risk?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines emphasise individualised targets and suggest stepping up treatment when HbA1c reaches what value?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Match the non-insulin diabetic medication with its mechanism of action:
Sort elements
- Reduces peripheral insulin resistance and hepatic glucose output
- Increase insulin secretion, suppress glucagon production, slow gastric emptying
- Inhibit renal glucose reabsorption – lower glucose independent of insulin
- Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells
- Delays absorption of carbohydrates from small intestine
- Metformin
- GLP-1 analogues (e.g. liraglutide)
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin)
- Sulfonylureas (e.g. gliclazide)
- Acarbose (alpha-glucosidase inhibitor)
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Elective surgery should be delayed in a patient whose HbA1c is 75 mmol/mol, true or false?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
The American Diabetes Association recognises three levels of hypoglycaemia, match the levels with their definition:
Sort elements
- Glucose level: <3.9mmol/L
- Glucose level: <3.0mmol/L
- A severe event characterised by altered mental and/or physical status (rather than a measurable glucose number) requiring assistance for treatment
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Differentiation between hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is often difficult as some patients with HHS may present with ketonuria. Which of the following statements about HHS and DKA are correct? (More than one answer may be correct)
CorrectIncorrect
- Citation
- The Pharmaceutical Journal, PJ, August 2024, Vol 313, No 7988;313(7988)::DOI:10.1211/PJ.2024.1.326780
1 comment
Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.



Very good quiz.