Shutterstock.com/Science Photo Library/various
Pharmacists play an important role in managing gastrointestinal (GI) conditions, providing medication education, monitoring potential drug interactions, and educating patients on lifestyle modifications that can help manage their GI symptoms, including dietary changes and adherence to medication regimens for conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastro-oesophageal reflux and diarrhoea.
Each question includes a link to a relevant article published in The Pharmaceutical Journal, providing more information on the topic. When you have answered all the questions, select ‘Finish quiz’ at the bottom of the page to check your score.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Case-based learning: constipation in adults’ (supported). Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
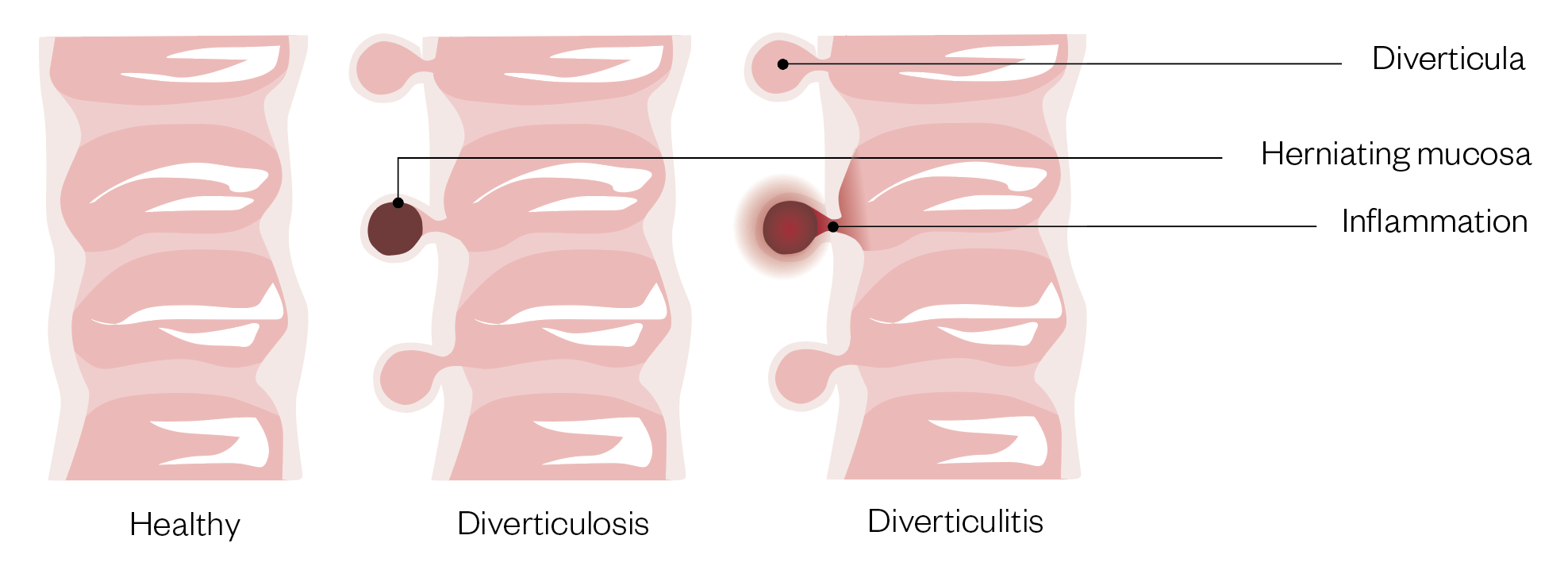
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: identification and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Diverticular disease and diverticulitis: causes, symptoms and treatment’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Management of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
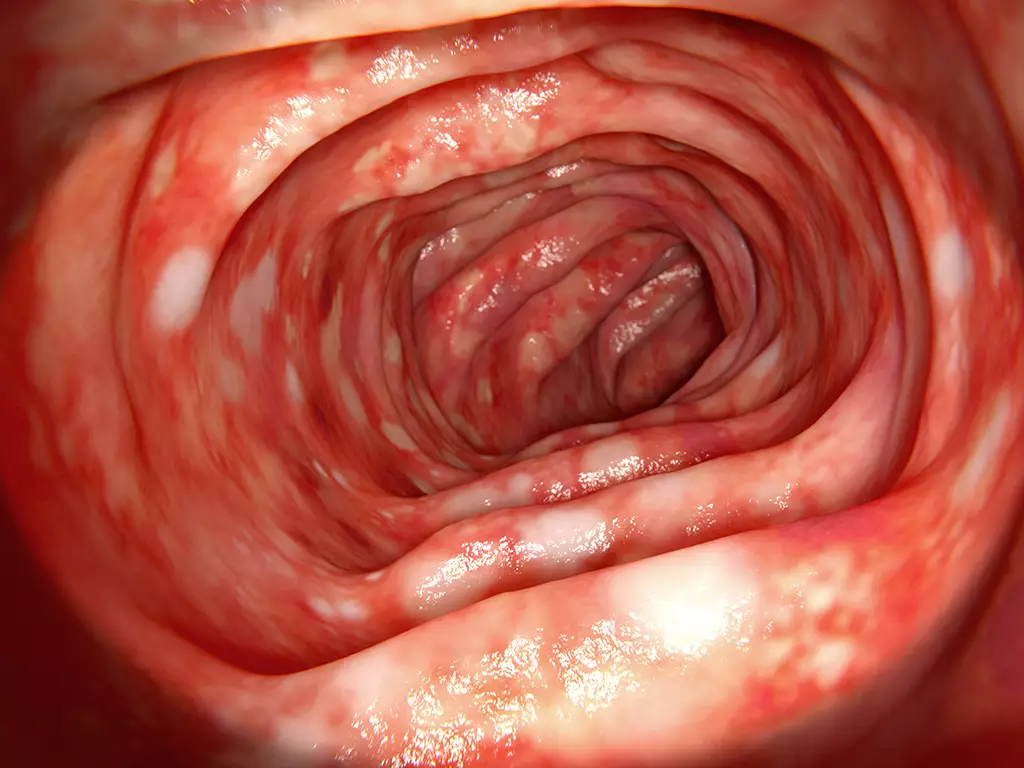
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Inflammatory bowel disease: symptoms and diagnosis’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Inflammatory bowel disease: treatment and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
BIOPHOTO ASSOCIATES/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
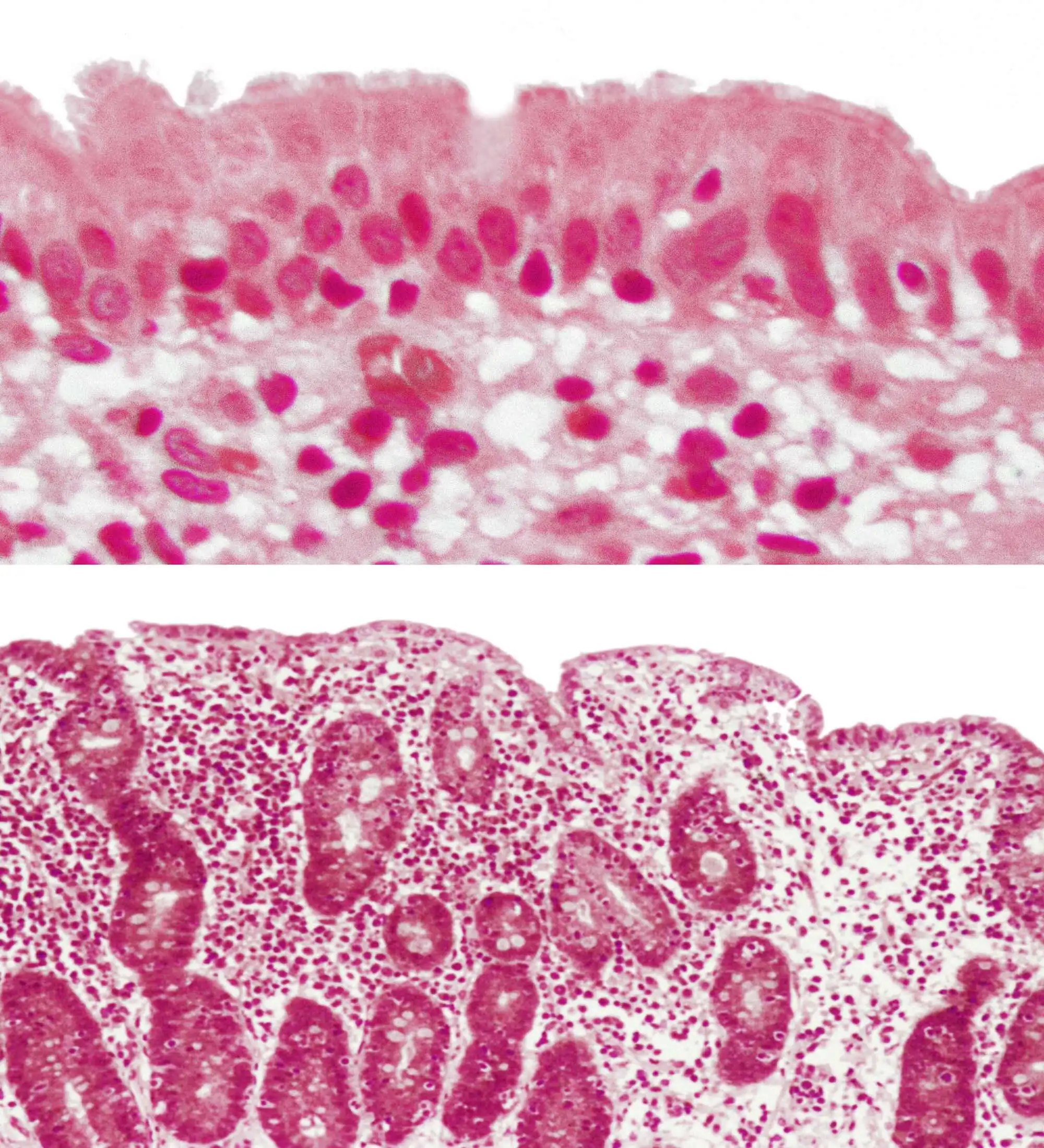
This question is from ‘How to identify symptoms of coeliac disease in community pharmacy and primary care’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Inflammatory bowel disease: symptoms and diagnosis’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
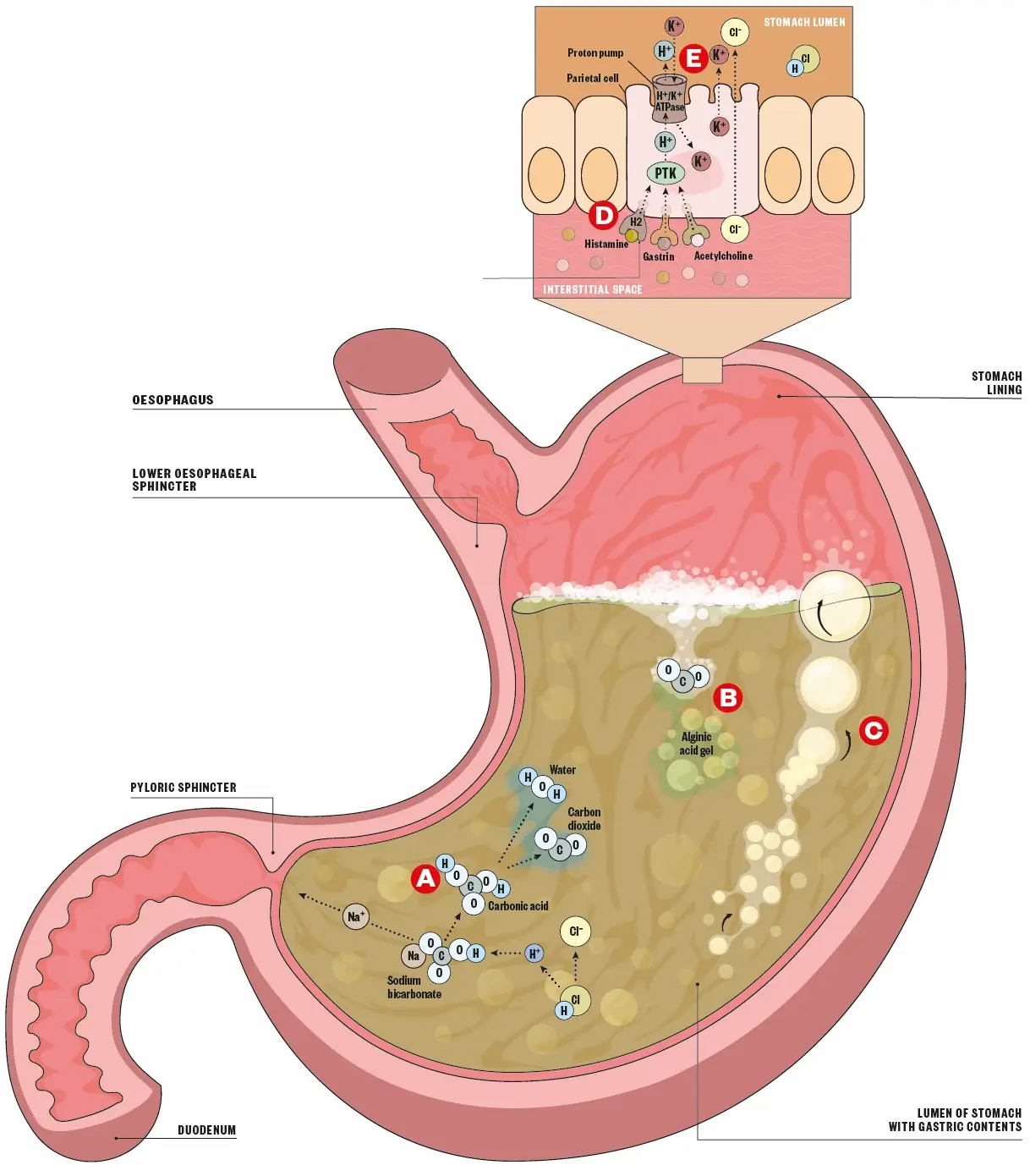
Alisdair Macdonald
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Relief from indigestion: a visual guide’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Victor de Schwanberg / Science Photo Library / reproduced with permission from Gut 2017;66(9):1631–1
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Colorectal cancer screening and the role of community pharmacy’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Case-based learning: haemorrhoids’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

MEHAU KULYK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Signs, symptoms and management of pancreatitis’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Case-based learning: gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in adults’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.

SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Case-based learning: acute diarrhoea’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
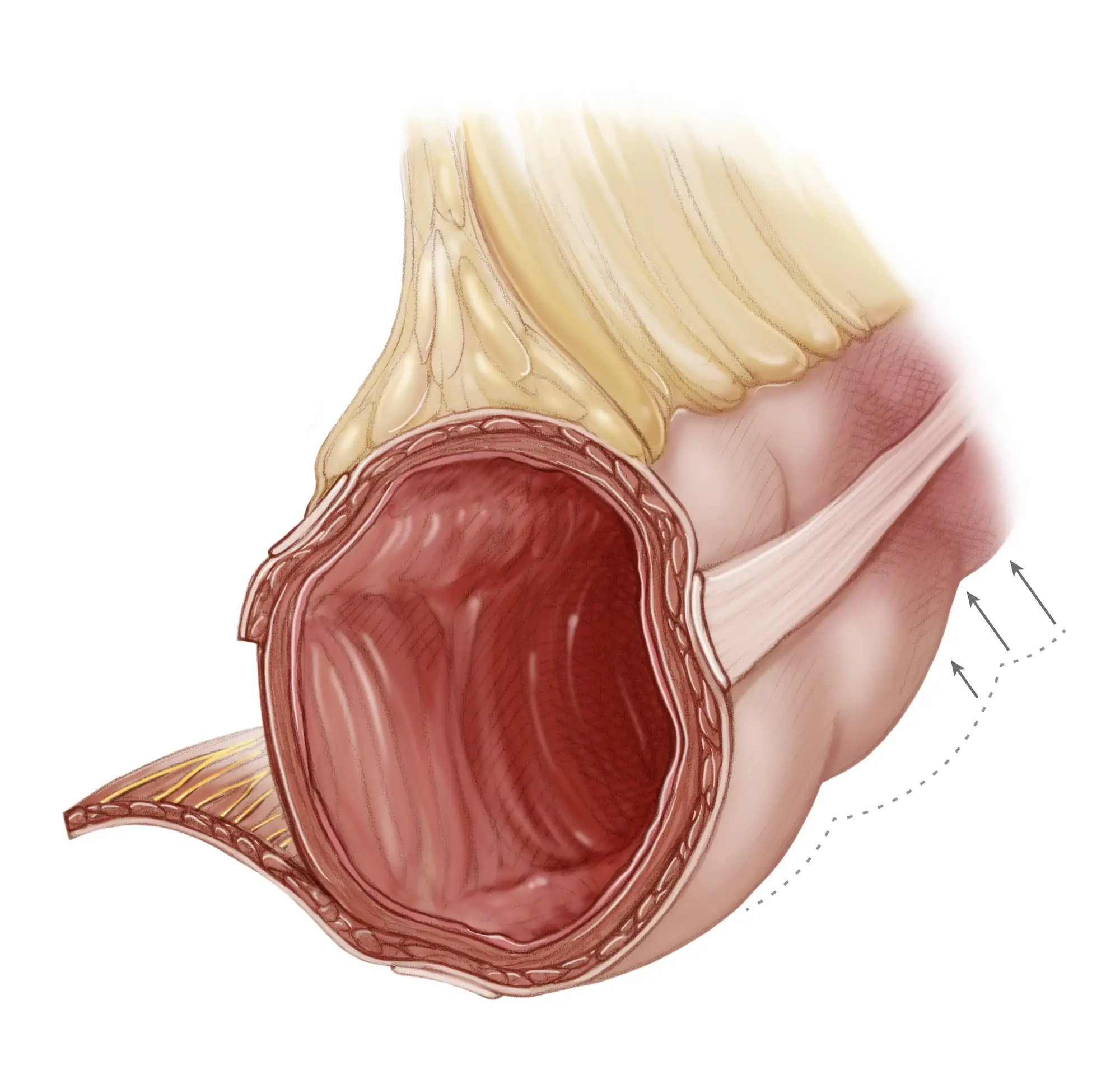
Alex Webber
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Untangling IBS from IBD’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
When treating constipation the aim of management is to resolve symptoms and help prevent future occurrence. This can typically be achieved by non-pharmacological measures, but treatment can be recommended if these are ineffective.
Which precautions should be taken when advising patients about over the counter measures for management of constipation to support correct use and minimise risk of misuse? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age groups and usually resolves with time. However it is important to know when a referral or further investigation may be required.
Match the following red-flag symptoms with the correct possible diagnostic implication:
Sort elements
- May suggest hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants aged up to two months
- Bacterial gastroenteritis or cow’s milk allergy
- Intestinal obstruction
- Bleeding from oesophagus, stomach or gut
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Frequent, forceful vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal distension, tenderness or palpable mass
- Blood in vomit
- Bulging fontanelle
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Diverticulosis is a digestive condition that mainly affects the sigmoid colon. Diverticulosis develops when a section of the mucosa pushes out or herniates through a weak area of muscle in the wall of the colon.
Which of the following symptoms are differentials that indicate a diagnosis of diverticular disease? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
Acute upper gastrointestinal bleed (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. A combination of both endoscopic and pharmacological treatments play an important role in reducing both mortality and morbidity arising from peptic ulcer and variceal bleeding, which are the most common underlying causes.
Which treatment should be started for secondary prevention of variceal bleeding?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are related diseases but there are contrasting features with regards to the clinical presentation, the site of involvement and extent of inflammation across the bowel wall.
Match the following clinical features and symptoms with the correct term.
Sort elements
- Shared feature
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Nutritional deficiencies, fatigue, weight loss
- Cramping pain, often before passing a stool
- Affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
In treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, ‘conventional therapy’ refers to which agents?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
It is estimated that in the UK there are more than 500,000 people with clinically undiagnosed coeliac disease, caused by an adverse immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When should testing for coeliac disease be considered? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
What diagnostic marker can be used to differentiate between inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Indigestion and heartburn affect four in ten people and there are various over the counter options available which can help to manage symptoms.
Look at the image above and match the labels A-E with the relevant class of medication.
Sort elements
- Antacids – acid binding group which neutralises stomach acid
- Alginates – reacts with gastric acid to produce foam that stops gastric acid flowing to oesophasgus
- Antiflatulents – reduces surface tension of bubbles to encourage expulsion through burping
- H2 receptor antagonists – bind to histamine receptors to reduce activation of proton pump
- Proton pump inhibitors – block the proton pump switching off gastric acid production
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following are symptoms of colorectal cancer that pharmacists should be aware of? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Referral to secondary care for consideration of further management of haemorrhoids may be indicated depending on the severity of symptoms and degree of prolapse.
Fill in the gaps in the sentence below selecting from the following options: II–IV, aggressive, conservative, III–V, ruptured, I–III, incarcerated, long-term
Referral to secondary care will usually be for haemorrhoids that have failed to respond to or have recurred despite management, are graded , or where the haemorrhoid is or thrombosed.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
The most common causes of pancreatitis can be remembered by using the acronym ‘GET SMASHED’. Fill in the blanks to complete the acronym below:
G
Ethanol
T
S
Mumps
Autoimmune disease
S
Hypercalcaemia and hyperlipidaemia
ERCP
Drugs
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which gastric contents reflux into the oesophagus, causing the patient to experience symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Which of the following describe the mechanisms of GORD? Select all that apply.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
When is testing for Clostridium difficile infection warranted for patients presenting with acute diarrhoea?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Complete the sentence below by selecting from the following terms: brain, microbiota, intestinal, pancreas, gastric
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of gut- interaction whereby emotional centres of the brain influence function. There is also emerging evidence that the is involved.
CorrectIncorrect
- Citation
- The Pharmaceutical Journal, PJ, February 2025, Vol 314, No 7994;314(7994)::DOI:10.1211/PJ.2025.1.345265