Shutterstock.com / Science Photo Library
It has been an exciting year for The Pharmaceutical Journal, with the launch of our new website and publication of the ‘Medicines in children and young people’ special issue in February. In this time of change we have continued to explore new content formats, such as our calculations video series. We have also increased our focus on the professional, or core, skills that pharmacists need to do their jobs and continue to develop as essential members of the multidisciplinary team — something that we will further develop in 2022.
Throughout 2021 we have continued to publish high quality resources to support pharmacists in their learning and development. This end-of-year quiz is broken down by clinical area, giving you the opportunity to improve your knowledge and identify any areas that may benefit from focused learning prior to revalidation. The answers to the quiz can be found at the end of this article.
Gastroenterology
1. What advice should be given to parents or carers looking after babies with acute diarrhoea?
a. Aspirin dissolved in water can be administered to manage a high temperature
b. Prepare baby formula at half the usual strength
c. Little sips of fizzy drink can be given to replace lost electrolytes
d. Give babies on formula or solid foods small sips of water between feeds
e. Refer to a GP if symptoms do not resolve within 24 hours
From: ‘Case-based learning: acute diarrhoea’
2. The Truelove and Witts’ severity index is a tool used to define the severity of ulcerative colitis in adults. Which of the following parameters is not used in the index?
a. Bowel movements
b. Anaemia
c. Blood in stool
d. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
e. C-reactive protein levels
From: ‘Inflammatory bowel disease: symptoms and diagnosis’
Paediatrics
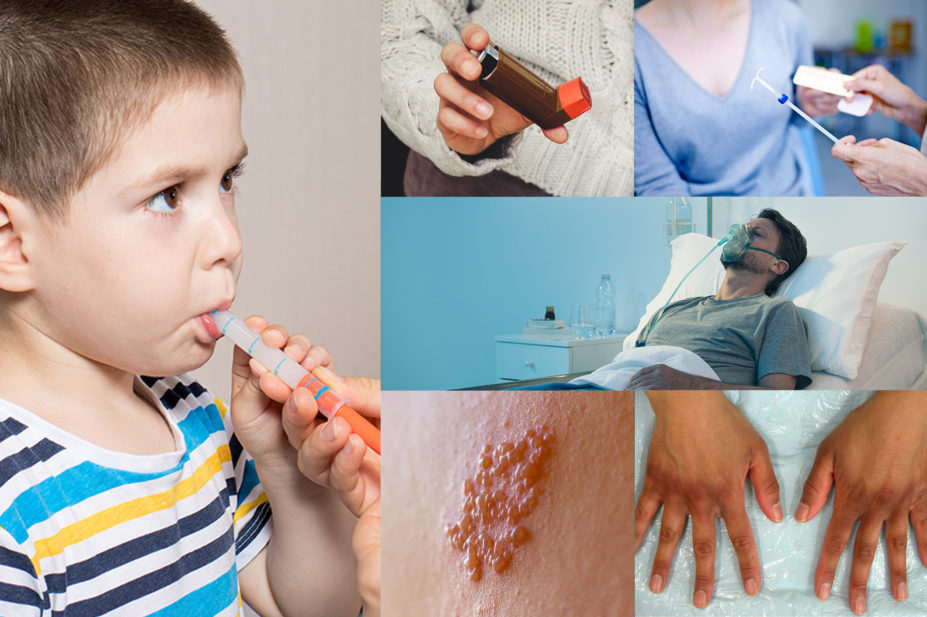
3. A parent presents to a pharmacy with their three-year-old child who has been experiencing mild fever and pain over the last 24 hours and asks what dose of paracetamol (120mg/5mL) should be given. Which of the following is correct?
a. 5mL four times daily
b. 7.5mL four times daily
c. 10mL four times daily
d. 15mL four times daily
e. 20mL four times daily
From: ‘Paracetamol use in infants and young children’
Shutterstock.com
4. Transition of young patients from paediatric to adult health care services is defined as “the purposeful, planned process that addresses the medical, psychosocial and educational/vocational needs of adolescents and young adults with chronic physical and medical conditions as they move from child-centred to adult-oriented healthcare systems”. At what age should the transition planning process for young patients begin?
a. Between 7–8 years
b. From the time the young person enters paediatric services
c. Between 11–12 years
d. At 18 years
e. There is no optimum age to commence transition planning
From: ‘Transition of care to adult services’
Women’s health
5. A new mother is experiencing severe pain after giving birth, she is breastfeeding her child. Which opioid option would be preferred?
a. Codeine
b. Dihydrocodeine
c. Tramadol
d. Oxycodone
e. Fentanyl
From: ‘How to advise women on the safe use of medicines while breastfeeding’
6. Which long-acting reversible contraceptive can be inserted for use as emergency contraception?
a. Copper intrauterine device
b. Etonogestrel implant
c. Progestogen-only contraceptive depot injection
d. 52mg levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system
e. 19.5mg levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system
From: ‘Long-acting reversible contraception‘
Alice S / BSIP / Science Photo Library
Dermatology
7. A patient presents to a pharmacy with dark brown patches across their knuckles & describes experiencing inflammation, itching and redness a week earlier (see image). What would be the diagnosis?
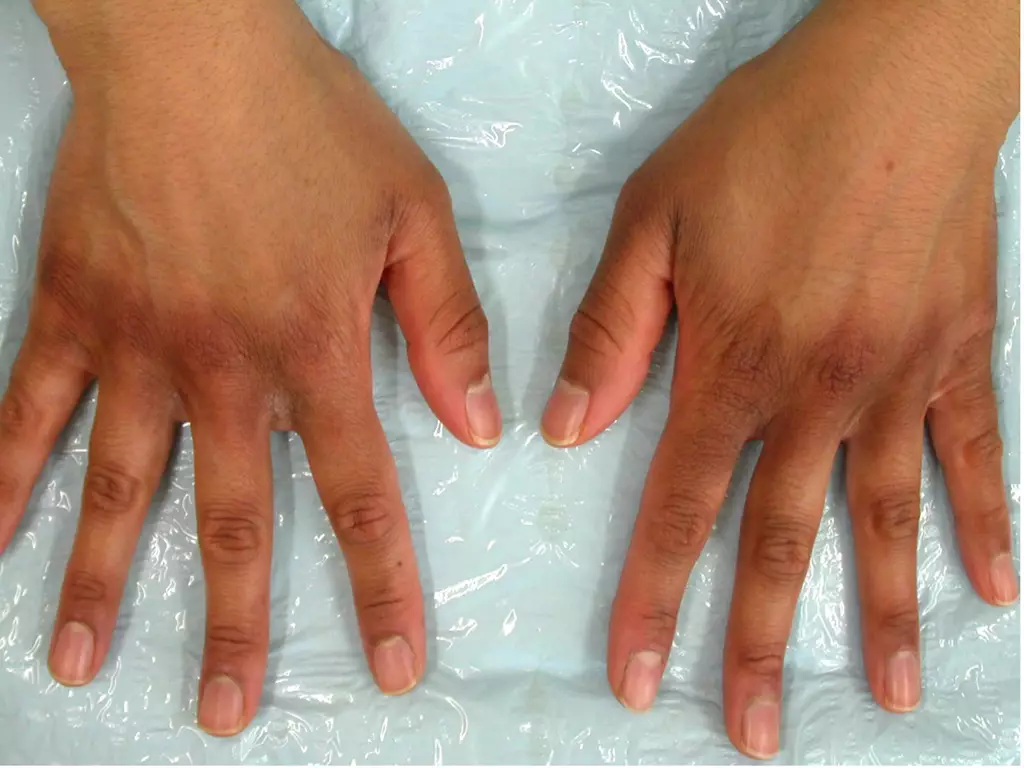
Demnet New Zealand
a. Lichen planus pigmentosus
b. Psoriasis
c. Melasma
d. Eczema
e. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
From: ‘Common dermatological conditions in skin of colour’
8. Which of the following images displays a maculopapular shingles rash?
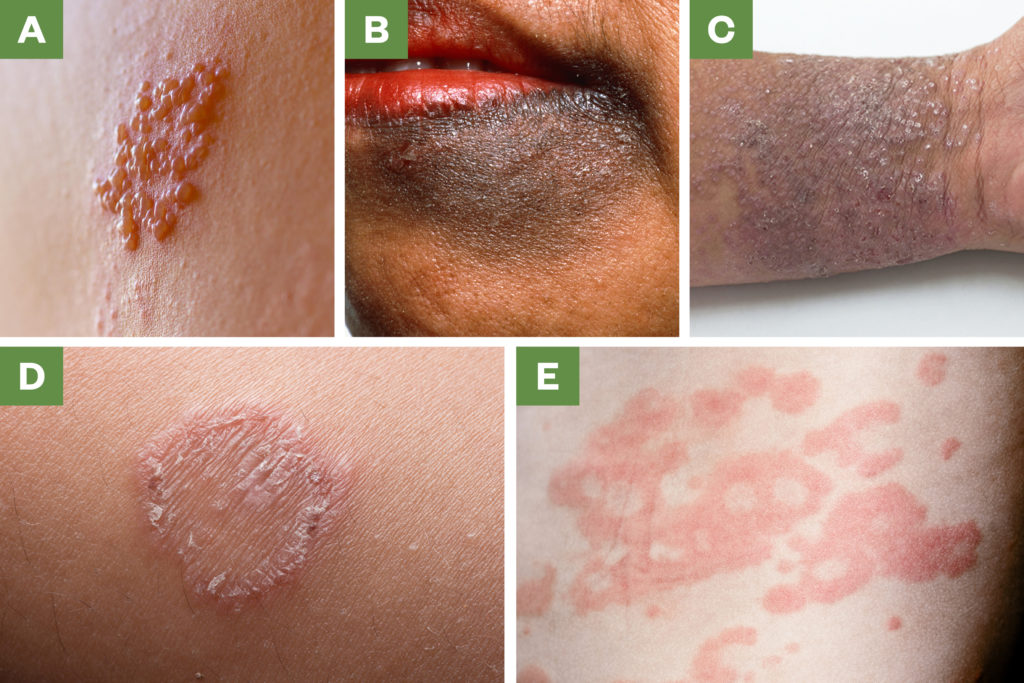
Shutterstock.com / Dr P Marazzi / Choksawatdikorn / Science Photo Library
From: ‘Case-based learning: shingles’
Prescribing errors
9. Feedback is an essential resource for promoting prescribing safety, and opportunities to deliver it should be increased. Which of the following does not constitute best practice in delivering effective feedback to an individual on their prescribing?
a. Enquiring on the prescriber’s experience and confidence in performing calculations
b. Encouraging discussion and reflection using open questions
c. Judging the prescriber’s performance or compare/rate them against other people
d. Delivering specific individualised feedback verbally and in written form
e. Providing evidence of prescriber performance in the form of audit and example prescriptions
From: ‘Prescribing errors in children: why they happen and how to prevent them’
COVID-19
10. What does the term ‘long-COVID’ refer to?
a. An unofficial term used to describe both ongoing symptomatic COVID-19 and post-COVID syndrome, where clusters of symptoms often overlap, fluctuate and change over time
b. Signs and symptoms that develop during or after an infection consistent with COVID-19, continue for more than 12 weeks and are not explained by an alternative diagnosis
c. New or persistent symptoms of COVID-19 that are experienced 4–12 weeks after initial onset and includes symptoms such as breathlessness, lethargy and weakness
d. The first four weeks following initial infection with SARs-CoV-2 that can affect multiple organ systems, in particular the respiratory system
e. Clusters of COVID-19 symptoms that overlap, fluctuate and change over a period of 24 – 36 months from the time of initial infection
From: ‘Managing the long-term effects of COVID-19‘
Respiratory tract conditions
11. What class of drugs should be used with care when combined with inhaled steroids due to the potential for increased blood steroid levels?
a. β-lactams
b. Triptans
c. Azoles
d. Tetracyclines
e. Echinocandins
From: ‘Uncontrolled asthma: assessment and management’

Shutterstock.com
12. Leukotriene receptor antagonists are often ineffective for preventing wheeze in pre-school children, however, they may be used in those whose parents are reluctant to use inhaled corticosteroids. Which side effects should prompt immediate cessation of treatment?
a. Headache and fatigue
b. Nausea and sickness
c. Pharyngitis and cough
d. Bruising and nosebleeds
e. Nightmares and behavioural changes
From: ‘Diagnosis and management of wheeze in pre-school children’
Professional skills
13. What type of work is considered the gold standard in clinical research studies and is missing from the evidence pyramid?
a. Randomised clinical trials
b. Cohort studies
c. Systematic reviews/meta-analyses
d. Animal studies
e. Case series
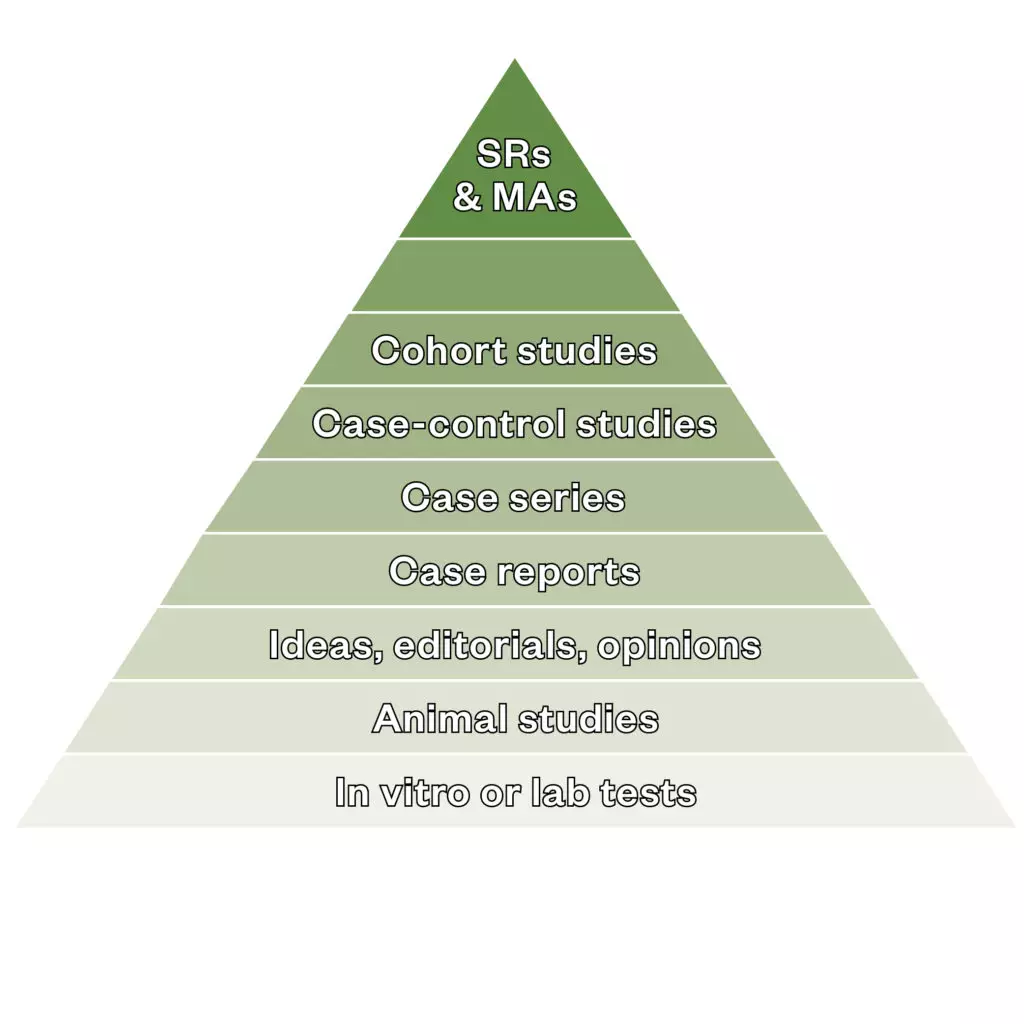
MA: meta-analyses; SR: systematic reviews.
From: ‘Critical appraisal: how to evaluate research for use in clinical practice’
14. Which of the following is NOT one of the nine attributes that make up the Professional Attributes Framework that forms the basis for situational judgement tests for trainee pharmacists?
a. Resilience and adaptability
b. Inclusion and diversity
c. Professional integrity and ethics
d. Person-centred care
e. Quality management and organisation
From: ‘Oriel situational judgement test: what pharmacy students need to know’
15. In the General Pharmaceutical Council registration assessment, if there are no rounding instructions at the end of a question, what action should be taken?
a. Round the answer to the nearest whole number
b. Do not round the answer
c. Round the answer to one decimal place
d. The answer is a whole number, so no rounding is needed
e. Follow the rounding instructions of the previous question
From: ‘A guide to rounding for pharmacy students and trainees‘
Answers
| 1) d | 9) c |
| 2) e | 10) a |
| 3) b | 11) c |
| 4) c | 12) e |
| 5) b | 13) a |
| 6) a | 14) b |
| 7) e | 15) d |
| 8) a |
You might also be interested in…

The engagement imperative

Why Ramadan is a clinical opportunity for pharmacy
