Research suggests that medication errors are more common in children and young people than in adults, as well as being more likely to cause harm. It is therefore vital that pharmacists across all sectors have the appropriate knowledge and skills to feel confident when treating this vulnerable patient population.
This quiz has been designed to complement the new paediatric health hub page. It is divided into three categories: medicines, conditions, and safeguarding and wellbeing. Each question includes a link to a relevant Pharmaceutical Journal article providing more information on the topic. Work your way through the quiz by expanding the questions in the boxes below. When you have answered all the questions, select ‘Finish quiz’ at the bottom of the page to see your score.
Medicines use
Excipients
Children may not be able to metabolise or eliminate excipients in the same way as adults owing to physiological and developmental differences. Expand question 1 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘How to identify and manage ‘problem’ excipients in medicines for children’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Corticosteroids
Hydrocortisone is a corticosteroid that is essential for the management of adrenal insufficiency, severe acute asthma and acute hypersensitivity reactions in paediatrics. Expand question 2 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The paroxysmal phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The convalescent phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Formulation matters: safe oral hydrocortisone use in children’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
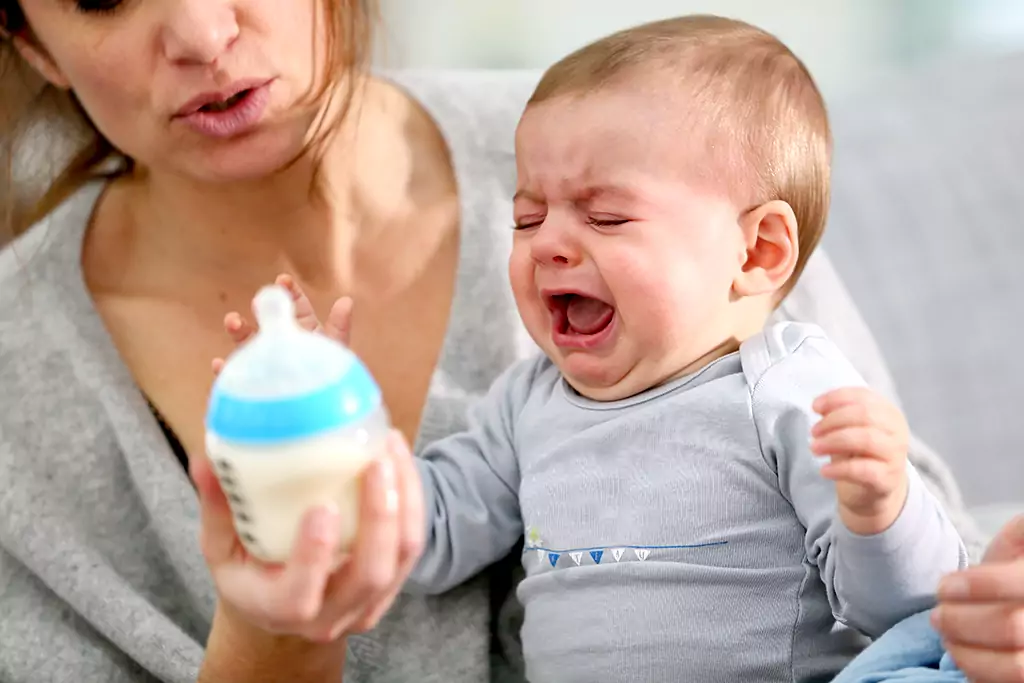
Analgesics
Paracetamol is one of the most used medicines in children; however, there are reports of adverse effects associated with unintentional overdosing. Expand question 3 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Paracetamol use in infants and young children’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Adverse drug reactions
Historically, children were believed to be at a lower risk of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) than adults; however, it is now known that children are at an equal, if not greater, risk of ADRs compared with adults. Expand question 4 to test your knowledge.
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The paroxysmal phase
- The catarrhal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Adverse drug reactions in children and young people’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Prescribing errors
Paediatric prescribing errors affect around 13% of paediatric prescriptions and can have lethal consequences. Expand question 5 to test your knowledge.

Josh Sher / Science Photo Library
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The paroxysmal phase
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Prescribing errors in children: why they happen and how to prevent them’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Vaccination
Despite the proven efficacy of vaccines, vaccine hesitancy is a growing concern, both in the UK and worldwide. Advice and recommendations from healthcare professionals are the most common reasons for vaccine-hesitant parents to reconsider. Expand question 6 to test your knowledge.
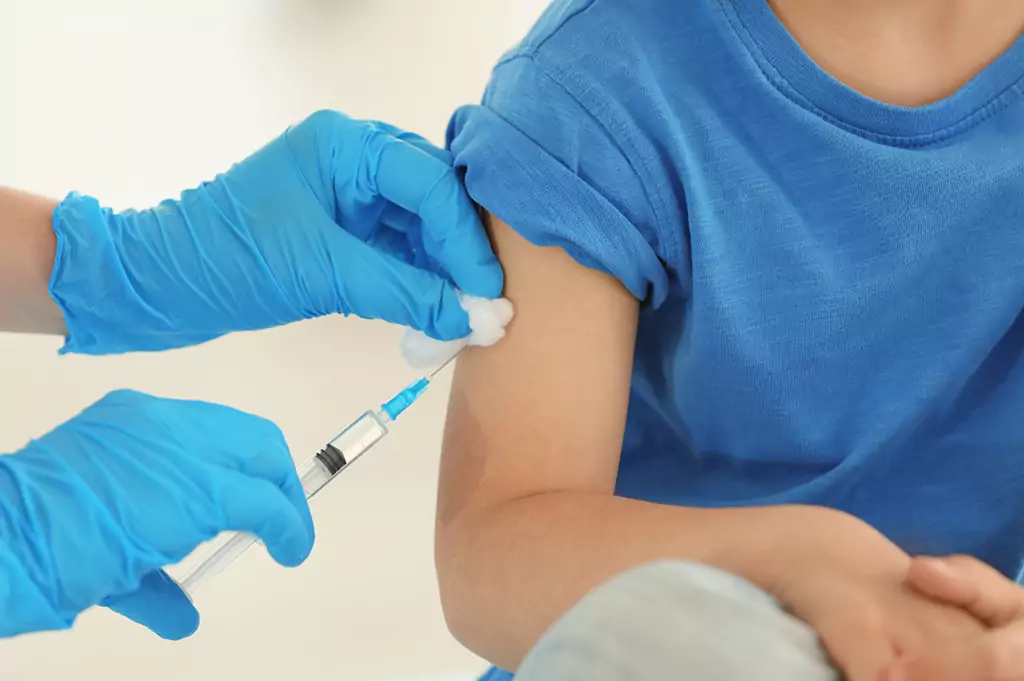
Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The catarrhal phase
- The convalescent phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘How to address vaccine hesitancy‘. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Conditions
Dermatology
Childhood rashes are common and most will disappear without the need for treatment. Expand question 7 to test your knowledge.

DR P. MARAZZI / ISM / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The paroxysmal phase
- The catarrhal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Rashes in children’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Respiratory
Whooping cough causes a prolonged cough illness without fever, with more severe disease being more common in young people. Expand question 8 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The paroxysmal phase
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Whooping cough: public health management and guidance‘. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Eye health
Vision development begins prenatally and continues after birth. Expand question 9 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Vision and eye health in children’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Parasites
While it is difficult to know how many cases there currently are in the UK, headlice infestation is common in school age children. Expand question 10 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The paroxysmal phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The convalescent phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Head lice: resistance and treatment options’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Gastroenterology
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease occurs when the reflux of gastric contents causes adverse symptoms and/or complications. It is one of the most common causes of foregut symptoms across all paediatric age ranges. Expand question 11 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: identification and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
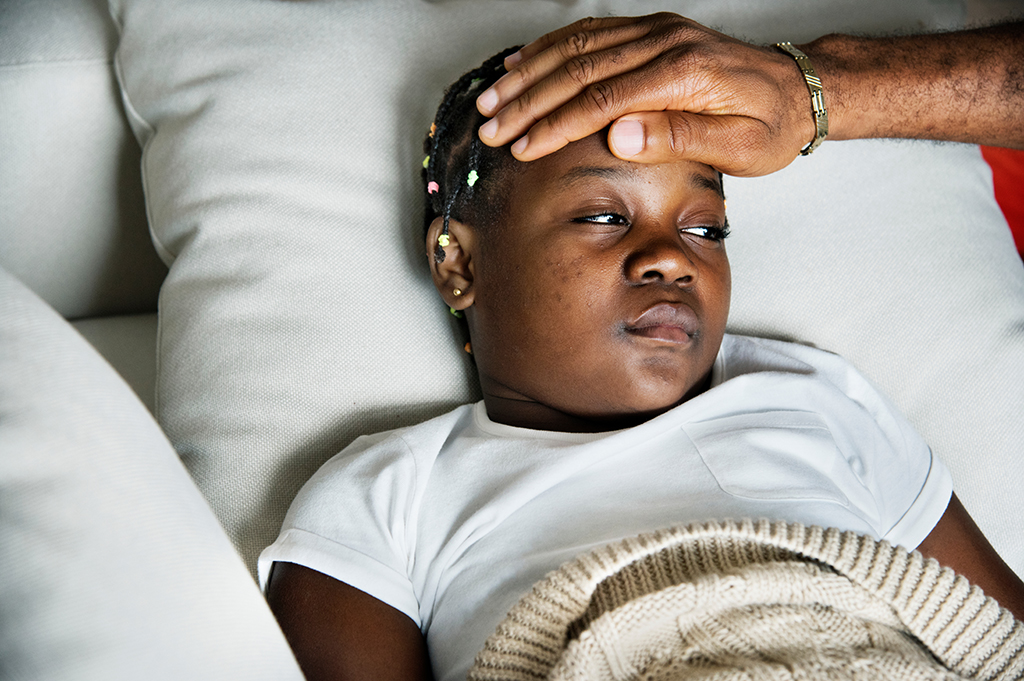
Symptom management
Fever is common in children and is a symptom seen in many conditions, including chickenpox. Expand question 12 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The paroxysmal phase
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Managing fever in children’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
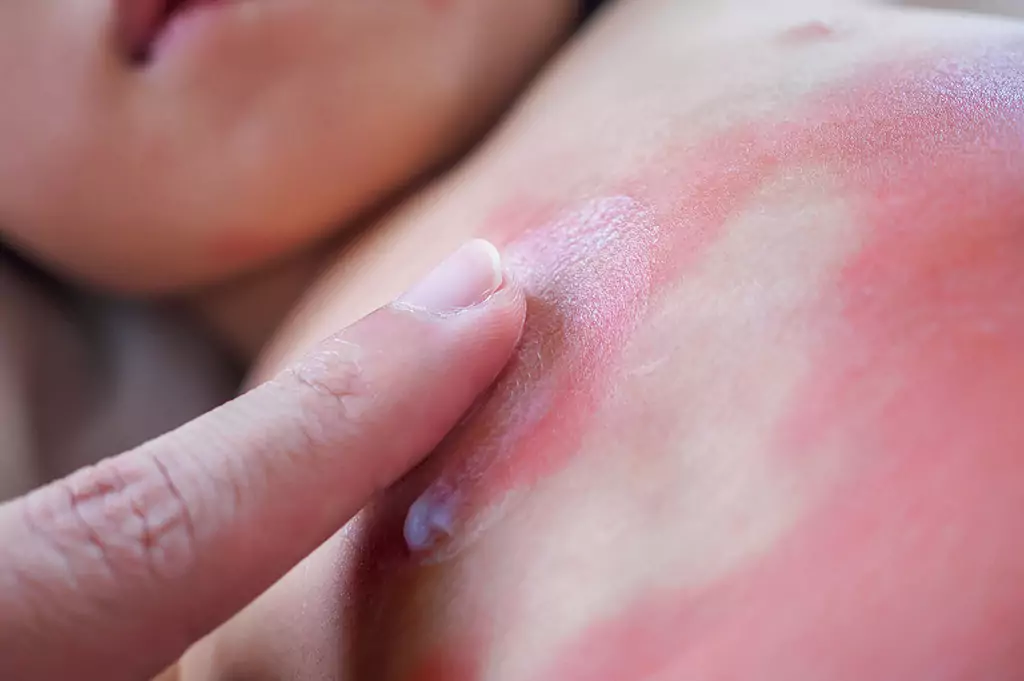
Infectious diseases
Scarlet fever is caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria. Expand question 13 to test your knowledge.
With permission from Skin Deep
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Everything you need to know about group A streptococcus infections’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Transitions and wellbeing
Transitions in care
The need to transition from paediatric to adult healthcare services is a challenge for many young people. Expand question 14 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Transition of care for young people moving to adult healthcare services’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Mental health
Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services provides coordinated care across sectors. There are four tiers within CAMHS, offering different areas of specialism. Expand question 15 to test your knowledge.

Shutterstock.com
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The convalescent phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The paroxysmal phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
This question is from ‘Depression in children and young people: identification and management’. Please refer to the original article if you would like to know more.
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
- Question 1 of 15
1. Question
Match the excipient with the potential adverse effect in children.
Sort elements
- Severe anaphylactoid reaction
- Jaundice in neonates
- Wheezing, dyspnoea and chest tightness in asthmatic children
- Osmotic diarrhoea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Hypersensitivity and photosensitivity reactions
- Polyoxyl castor oil
- Benzoic acid
- Sodium metasulfites
- Sorbitol
- Saccharin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 2 of 15
2. Question
Fill in the blanks in the following passage:
Hydrocortisone tablets are available in strengths of 10mg and 20mg in the UK, with some 10mg tablets scored to allow splitting to doses. Although quartering these tablets is licensed, concerns have been highlighted around the of doses, with as many as 54% of doses falling outside the error margin
CorrectIncorrect - Question 3 of 15
3. Question
Paracetamol is currently recommended for post-immunisation fever in children following which vaccination?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 4 of 15
4. Question
What group of medicines are most reported in ADRs for children and young people?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 5 of 15
5. Question
Select all of the following that are examples of paediatric-specific causes of errors.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 6 of 15
6. Question
Fill in the blanks:
The ‘3 Cs’ model can be used to conceptualise vaccine hesitancy. refers to lack of trust in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines and the system through which they are delivered. refers to the low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, leading to an assumption that vaccines are not needed. refers to the degree that physical availability, affordability, willingness-to-pay, geographical accessibility and ability to understand (language and health literacy) influence uptake of the vaccine.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 7 of 15
7. Question
Look at the above examples of common rashes in children and match them with the correct answer.
Sort elements
- Chickenpox
- Heat rash
- Hand, foot and mouth
- Eczema
- Hives
- A.
- B.
- C.
- D.
- E.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 8 of 15
8. Question
Whooping cough can be divided into three phases of symptom, drag the options to put these phases into the correct order.
- The paroxysmal phase
- The catarrhal phase
- The convalescent phase
View:
CorrectIncorrect - Question 9 of 15
9. Question
Select all the following that are examples of refractive error eye disorders.
CorrectIncorrect - Question 10 of 15
10. Question
Which of the following treatment options are affected by resistance and should not be recommended?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 11 of 15
11. Question
Which prokinetic agent is no longer used to treat GORD in paediatric patients due to concerns of arrythmias in some children?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 12 of 15
12. Question
Which drug class should not be recommended with the sole aim of reducing body temperature in children with fever?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 13 of 15
13. Question
What symptom of scarlet fever is shown in the image above?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 14 of 15
14. Question
At what age does National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidance suggest transition planning should begin?
CorrectIncorrect - Question 15 of 15
15. Question
Match the tier with the relevant services and experts:
Sort elements
- Primary care services, including GPs, paediatricians, health visitors, school nurses, social workers, teachers, juvenile justice workers, voluntary agencies and social services;
- CAMHS is provided by professionals working with primary care, including clinical child psychologists, paediatricians with specialist training in mental health, educational psychologists, child and adolescent psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychotherapists, counsellors, community nurses or nurse specialists, and family therapists;
- CAMHS specialised services for more severe, complex or persistent disorders, including child and adolescent psychiatrists, clinical child psychologists, nurses or nurse specialists (community or hospital based), child and adolescent psychotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, art, music and drama therapists, and family therapists;
- Tertiary-level services (e.g. day units, highly specialised outpatient teams and inpatient units). The availability of services will vary depending on locality but all children should be seen by a specialist with experience in child and adolescent mental health.
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
CorrectIncorrect
- Citation
- The Pharmaceutical Journal, PJ, March 2023, Vol 310, No 7971;310(7971)::DOI:10.1211/PJ.2023.1.176981
2 comments
Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.


Excellent quiz but not sure if the answers to question 7 (rashes) are correct. Can the PJ please review this?
Thank you for bringing this to our attention. The question has been reviewed to ensure that the answers accurately reflect the rashes pictured.
Michael Dowdall - Executive Editor, Research & Learning